Monetary Policy:
Central Bank tries to prevent crowding out by monetizing budget deficit. To increase the effectiveness of monetary policy, monetary accommodation is used.
Monetary accommodation means that in the course of fiscal expansion, money supply is increased in order to prevent interest rate from rising. It is also known as monetizing budget deficit.
Due to fiscal expansion in an economy with unemployed resources, AD will increase. It will lead to decrease in inventories.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Result:
Firms will expand the output. This will lead to an increase in the income level. When income level increases, both consumption and saving will increase because Y = C + S. Since savings is a function of the income level, savings will increase. This saving will be used to meet a large part of budget deficit without completely displacing the private spending, that is, only some amount of private investment will be crowded out.
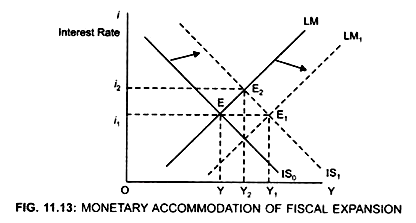
Movement from E to E1 and then from E1 to E2 shows partial crowding out. Since the economy is operating at less than full employment level, there is possibility of output to expand without increasing the interest rate. Thus it is not essential that when the Government expenditure rises, there will be any crowding out.
[AD ↑ with AO constant → AD > AO → Inventories↓→ output ↑ → income ↑. But when Y↑ → C ↑ → S ↑. This ↑ saving used to meet budget deficit. Saving(s) is not related to investment. Therefore, some investment is crowded out.]
ADVERTISEMENTS:
According to R. Dornbush and S. Fischer: “The monetary policy is, thus, accommodating when in course of fiscal expansion the money supply is increased to prevent interest rate from rising”.
Due to fiscal expansion, IS curve shifts to the right from IS0 to IS1 and the Government runs into deficit. To meet this deficit the Central Bank prints money to buy the bonds with which the Government pays for its deficit. This will lead to an increase in the money supply. As a result, LM curve shifts to the right to LM1. Thus, when Central Bank accommodates fiscal expansion, both IS and LM curve will shift to the right [Fig 11.13] to IS1, and LM1. Although the output increases from Y to Y1 but the interest rate does not increase and thus there will be no adverse effect, there is no crowding out effect on the Investment and income.
Thus, although the income level has increased, yet the interest rate does not increase rather it remains the same and, therefore, there will be no crowding out.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Government can prevent crowding out either by:
(a) Increase in the Government spending or decrease in taxes which will increase the consumption spending and, thus, AD, or
(b) Through Investment subsidy.
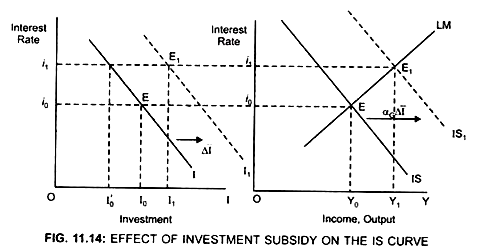
Assume the Government gives an Investment tax credit:
Due to investment tax credit, the level of investment spending increases because a part of cost of investment is borne by the Government. Therefore, due to investment tax credit, the Investment curve will shift to the right from I to I1 (Fig. 11.14)
This shows that at a given interest rate (i0) firms will invest more.
Result:
AD will increase.
Choice of Policy to Reach Full Employment Level or the Policy Mix:
The question of policy mix arises because on the one hand.
Expansionary monetary Policy → Increases the income level but decreases the interest rate on the other hand, expansionary Fiscal Policy → Increases both the income level and the interest rate.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
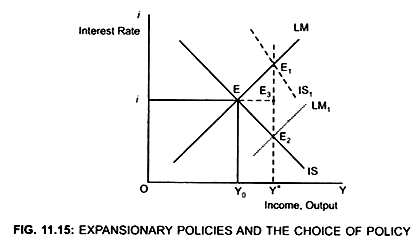
Initially the economy is in equilibrium at less than full employment level (Y0). This corresponds to point E (Fig. 11.15). In order to reach full employment level (Y*) the economy has following options:
Choice of Policy to reach full employment output Y
(i) Chose Expansionary Fiscal Policy:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Equilibrium point will move from point E to E1
Both interest rate and the income level increases.
Full employment will be achieved at higher income level and higher interest rate. Thus, due to expansionary fiscal policy both interest rate and the income level increases.
(ii) Chose Expansionary Monetary Policy:
Equilibrium point will move from point E to E2.
Full employment will be achieved at higher income level but low interest rate. Thus, due to expansionary monetary policy Interest rate decreases and the income level increases.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iii) Use both expansionary monetary and fiscal policy:
In this case economy will move from point E to E3 where interest rate and investment would remain unchanged but output level will increase.
Choice of policy will depend on the political preferences. The policy makers, however, should choose a combination of fiscal and monetary policies which would not only bring the economy to full employment level but also help to solve other policy problems.