In economics the terms change in quantity demanded and change in demand are two different concepts.
Change in quantity demanded refers to change in the quantity purchased due to increase or decrease in the price of a product.
In such a case, it is incorrect to say increase or decrease in demand rather it is increase or decrease in the quantity demanded.
On the other hand, change in demand refers to increase or decrease in demand of a product due to various determinants of demand, while keeping price at constant.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Changes in quantity demanded can be measured by the movement of demand curve, while changes in demand are measured by shifts in demand curve. The terms, change in quantity demanded refers to expansion or contraction of demand, while change in demand means increase or decrease in demand.
1. Expansion and Contraction of Demand:
The variations in the quantities demanded of a product with change in its price, while other factors are at constant, are termed as expansion or contraction of demand. Expansion of demand refers to the period when quantity demanded is more because of the fall in prices of a product. However, contraction of demand takes place when the quantity demanded is less due to rise in the price o a product.
For example, consumers would reduce the consumption of milk in case the prices of milk increases and vice versa. Expansion and contraction are represented by the movement along the same demand curve. Movement from one point to another in a downward direction shows the expansion of demand, while an upward movement demonstrates the contraction of demand.
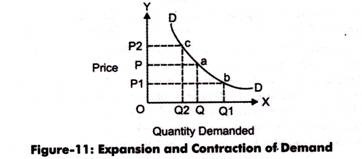
Figure-11 demonstrates the expansion and contraction of demand:
When the price changes from OP to OP1 and demand moves from OQ to OQ1, it shows the expansion of demand. However, the movement of price from OP to OP2 and movement of demand from OQ to OQ2 show the contraction of demand.
2. Increase and Decrease in Demand:
Increase and decrease in demand are referred to change in demand due to changes in various other factors such as change in income, distribution of income, change in consumer’s tastes and preferences, change in the price of related goods, while Price factor is kept constant Increase in demand refers to the rise in demand of a product at a given price.
On the other hand, decrease in demand refers to the fall in demand of a product at a given price. For example, essential goods, such as salt would be consumed in equal quantity, irrespective of increase or decrease in its price. Therefore, increase in demand implies that there is an increase in demand for a product at any price. Similarly, decrease in demand can also be referred as same quantity demanded at lower price, as the quantity demanded at higher price.
Increase and decrease in demand is represented as the shift in demand curve. In the graphical representation of demand curve, the shifting of demand is demonstrated as the movement from one demand curve to another demand curve. In case of increase in demand, the demand curve shifts to right, while in case of decrease in demand, it shifts to left of the original demand curve.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Figure-12 shows the increase and decrease in demand:
In Figure-12, the movement from DD to D1D1 shows the increase in demand with price at constant (OP). However, the quantity has also increased from OQ to OQ1.
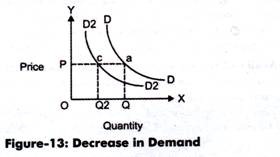
Figure-13 shows the decrease in demand:
In Figure-13, the movement from DD to D2D2 shows the decrease in demand with price at constant (OP). However, the quantity has also decreased from OQ to OQ2.