This article will help you to learn about the difference between Market Price and Normal Price.
Difference between Market Price and Normal Price
(1) Market price is that price which prevails in a market on a single day or on very few days. It is a very short-period price which prevails at a particular time. On the other hand, normal price is that price which tends to prevail in the long-run. It is a price which has a tendency to prevail over a period of time.
(2) In the determination of market price, demand plays an active role while supply is passive. The market price rises or falls with the rise of fall in demand while supply is fixed. On the other hand, supply is more active in the determination of normal price because it tends to adjust itself fully to any change in demand.
(3) Market price is influenced by temporary events. It may change many times a day or a week as a result of passing events. A sudden rainfall on a hot day may bring down the demand for ice, and hence lower its price. Thus market price exists only temporarily and its equilibrium is also temporary.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Normal price, on the other MP hand, is the outcome of permanent forces which bring about changes in demand and supply. Demand may change due to changes in tastes, habits, preferences, etc. of consumers, while supply may change by altering the fixed factors of production.
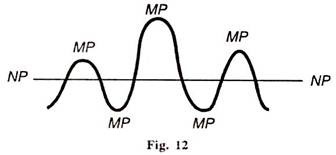
Normal price is thus a permanent and stable price which has permanent equilibrium. Market price, therefore, tends to show oscillations around normal price, as shown in Figure 12 it where NP denotes normal and MP market price.
(4) Market price can be above or below the average cost of production. Hence firms can earn supernormal profits or incur losses. On the other hand, normal price is always equal to the long-run average cost (LAC) at its minimum point. Therefore, firms can earn only normal profits under normal price.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(5) All commodities whether reproducible or non-reproducible have market price. But only reproducible commodities have normal price. If a commodity is non-reproducible, its supply cannot be increased in the long-run when its demand increases.
For instance, a painting done by Tagore lying with a curios dealer cannot have normal price because Tagore is no longer alive to repaint the like of it. It can only be sold at the market price which it fetches at a particular time.
(6) Market price is the real price which prevails in the market at any time. On the other hand, normal price is a hypothetical price. It is an abstraction, a myth. Something unreal and imaginary. It is like a mirage. The small waves in the sea are real but the calm water of the sea in the distant horizon is like a mirage.
The small waves represent the market price while the calm water in the distant, the normal price.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
As pointed out by Stonier and Hague, “In practice, a long period normal price will never be arrived at. There will usually be a change in some of the conditions underlying the long period equilibrium before it has had time to come into being. The long-run like tomorrow never comes” and the price that rules in the market is always the market price rather than the normal price.