Let us make in-depth study of the meaning, phases and features of business cycles.
Meaning of Business Cycle:
The period of high income, output and employment has been called the period of expansion, upswing or prosperity, and the period of low income, output and employment has been described as contraction, recession, downswing or depression.
The economic history of the free market capitalist countries has shown that the period of economic prosperity or expansion alternates with the period of contraction or recession.
These alternating periods of expansion and contraction in economic activity has been called business cycles. They are also known as trade cycles. J.M. Keynes writes, “A trade cycle is composed of periods of good trade characterized by rising prices and low unemployment percentages with periods of bad trade characterized by falling prices and high unemployment percentages.”
ADVERTISEMENTS:
A noteworthy feature about these fluctuations in economic activity is that they are recurrent and have been occurring periodically in a more or less regular fashion. Therefore, these fluctuations have been called business cycles. It may be noted that calling these fluctuations as ‘cycles’ means they are periodic and occur regularly, though perfect regularity has not been observed.
The duration of a business cycle has not been of the same length; it has varied from a minimum of two years to a maximum of ten to twelve years, though in the past it was often assumed that fluctuations of output and other economic indicators around the trend showed repetitive and regular pattern of alternating periods of expansion and contraction.
However, actually there has been no clear evidence of very regular cycles of the same definite duration. Some business cycles have been very short lasting for only two to three years, while others have lasted for several years. Further, in some cycles there have been large swings away from trend and in others these swings have been of moderate nature.
A significant point worth noting about business cycles is that they have been very costly in the economic sense of the word. During a period of recession or depression many workers lose their jobs and as a result large-scale unemployment, which causes loss of output that could have been produced with full employment of resources, come to prevail in the economy.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Besides, during depression many businessmen go bankrupt and suffer huge losses. Depression causes a lot of human sufferings and lowers the levels of living of the people. Fluctuations in economic activity creates a lot of uncertainty in the economy which causes anxiety to the individuals about their future income and employment opportunities and involve a great risk for long-run investment in projects. Who does not remember the great havoc caused by the great depression of the early thirties of the present century?
Even boom when it is accompanied by inflation has its social costs. Inflation erodes the real incomes of the people and makes life miserable for the poor people. Inflation distorts allocation of resources by drawing away scarce resources from productive uses to unproductive ones. Inflation redistributes income in favour of the richer sections and also when inflation rate is high, it impedes economic growth.
About the harmful effects of the business cycles Crowther writes, “On the one hand, there is the misery and shame of unemployment with all the individual poverty and social disturbances that it may create. On the other hand, there is the loss of wealth represented by so much wasted and idle labour and capital.”
Phases of Business Cycles:
Business cycles have shown distinct phases the study of which is useful to understand their underlying causes. These phases have been called by different names by different economists.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Generally, the following phases of business cycles have been distinguished:
1. Expansion (Boom, Upswing or Prosperity)
2. Peak (upper turning point)
3. Contraction (Downswing, Recession or Depression)
4. Trough (lower turning point)
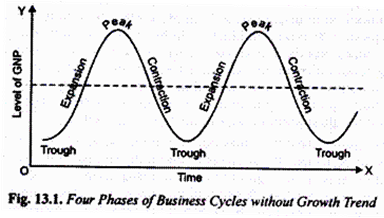
The four phases of business cycles have been shown in Fig. 13.1 where we start from trough or depression when the level of economic activity i.e., level of production and employment is at the lowest level.
With the revival of economic activity the economy moves into the expansion phase, but due to the causes explained below, the expansion cannot continue indefinitely, and after reaching peak, contraction or downswing starts. When the contraction gathers momentum, we have a depression. The downswing continues till the lowest turning point which is also called trough is reached.
In this way cycle is complete. However, after remaining at the trough for some time the economy revives and again the new cycle starts.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Haberler in his important work on business cycles has named the four phases of business cycles as:
(1) Upswing,
(2) Upper turning point,
(3) Downswing, and
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(4) Lower turning point.
There are two types of patterns of cyclic changes. One pattern is shown in Fig. 13.1 where fluctuations occur around a stable equilibrium position as shown by the horizontal line. It is a case of dynamic stability which depicts change but without growth or trend.
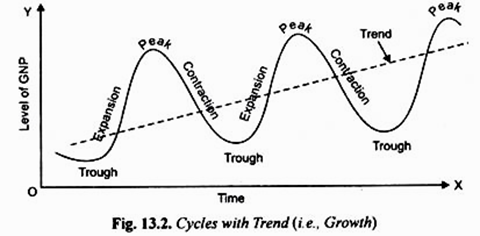
The second pattern of cyclical fluctuations is shown in Fig. 13.2 where cyclical changes in economic activity take place around a growth path (i.e., rising trend). J.R. Hicks in his model of business cycles explains such a pattern of fluctuations with long-run rising trend in economic activity by imposing factors such as autonomous investment due to population growth and technological progress causing economic growth on the otherwise stationary state. We briefly explain below various phases of business cycles.
Expansion and Prosperity:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In its expansion phase, both output and employment increase till we have full employment of resources and production is at the highest possible level with the given productive resources. There is no involuntary unemployment and whatever unemployment prevails is only of frictional and structural types.
Thus, when expansion gathers momentum and we have prosperity, the gap between potential GNP and actual GNP is zero, that is, the level of production is at the maximum production level. A good amount of net investment is occurring and demand for durable consumer goods is also high. Prices also generally rise during the expansion phase but due to high level of economic activity people enjoy a high standard of living.
Then something may occur, whether banks start reducing credit or profit expectations change adversely and businessmen become pessimistic about future state of the economy that brings an end to the expansion or prosperity phase. Economists differ regarding the possible causes of the end of prosperity and start of downswing in economic activity.
Monetarists have argued that contraction in bank credit may cause downswing. Keynes has argued that sudden collapse of expected rate of profit (which he calls marginal efficiency of capital, MEC) caused by adverse changes in expectations of entrepreneurs lowers investment in the economy. This fall in investment, according to him, causes downswing in economic activity.
Contraction and Depression:
As stated above, expansion or prosperity is followed by contraction or depression. During contraction, not only there is a fall in GNP but also level of employment is reduced. As a result, involuntary unemployment appears on a large scale. Investment also decreases causing further fall in consumption of goods and services.
At times of contraction or depression prices also generally fall due to fall in aggregate demand. A significant feature of depression phase is the fall in rate of interest. With lower rate of interest people’s demand for money holdings increases. There is a lot of excess capacity as industries producing capital goods and consumer goods work much below their capacity due to lack of demand.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Capital goods and durable consumer goods industries are especially hit hard during depression. Depression, it may be noted, occurs when there is a severe contraction or recession of economic activities. The depression of 1929-33 is still remembered because of its great intensity which caused a lot of human suffering.
Trough and Revival:
There is a limit to which level of economic activity can fall. The lowest level of economic activity, generally called trough, lasts for some time. Capital stock is allowed to depreciate without replacement. The progress in technology makes the existing capital stock obsolete. If the banking system starts expanding credit or there is a spurt in investment activity due to the emergence of scarcity of capital as a result of non-replacement of depreciated capital and also because of new technology coming into existence requiring new types of machines and other capital goods.
The stimulation of investment brings about the revival or recovery of the economy. The recovery is the turning point from depression into expansion. As investment rises, this causes induced increase in consumption. As a result industries start producing more and excess capacity is now put into full use due to the revival of aggregate demand. Employment of labour increases and rate of unemployment falls. With this the cycle is complete.
Features of Business Cycles:
Though different business cycles differ in duration and intensity, they have some common features which we explain below:
1. Business cycles occur periodically. Though they do not show same regularity, they have some distinct phases such as expansion, peak, contraction or depression and trough. Further the duration of cycles varies a good deal from minimum of two years to a maximum of ten to twelve years.
2. Secondly, business cycles are synchronic. That is, they do not cause changes in any single industry or sector but are of all-embracing character. For example, depression or contraction occur simultaneously in all industries or sectors of the economy.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Recession passes from one industry to another and chain reaction continues till the whole economy is in the grip of recession. Similar process is at work in the expansion phase, prosperity spreads through various linkages of input-output relations or demand relations between various industries, and sectors.
3. Thirdly, it has been observed that fluctuations occur not only in level of production but also simultaneously in other variables such as employment, investment, consumption, rate of interest and price level.
4. Another important feature of business cycles is that investment and consumption of durable consumer goods such as cars, houses, refrigerators are affected most by the cyclical fluctuations. As stressed by J.M. Keynes, investment is greatly volatile and unstable as it depends on profit expectations of private entrepreneurs.
These expectations of entrepreneurs change quite often making investment quite unstable. Since consumption of durable consumer goods can be deferred, it also fluctuates greatly during the course of business cycles.
5. An important feature of business cycles is that consumption of non-durable goods and services does not vary much during different phases of business cycles. Past data of business cycles reveal that households maintain a great stability in consumption of non-durable goods.
6. The immediate impact of depression and expansion is on the inventories of goods. When depression sets in, the inventories start accumulating beyond the desired level. This leads to cut in production of goods. On the contrary, when recovery starts, the inventories go below the desired level. This encourages businessmen to place more orders for goods whose production picks up and stimulates investment in capital goods.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
7. Another important feature of business cycles is that profits fluctuate more than any other type of income. The occurrence of business cycles causes a lot of uncertainty for businessmen and makes it difficult to forecast the economic conditions.
During the depression period profits may even become negative and many businesses go bankrupt. In a free market economy profits are justified on the ground that they are necessary payments if the entrepreneurs are to be induced to bear uncertainty.
8. Lastly, business cycles are international in character. That is, once started in one country they spread to other countries through trade relations between them. For example, if there is a recession in the USA, which is a large importer of goods from other countries, it will cause a fall in demand for imports from other countries whose exports would be adversely affected causing recession in them too. Depression of 1930s in USA and Great Britain engulfed the entire capital world.