Exports play a significant role in India’s trade as they help in earning foreign exchange.
In 16th century, India started exporting goods, such as spices and precious stones, including ivory and pearls to the other parts of the world. The exports of India declined during British rule.
However, from the last few years, due to liberalization and globalization, India has experienced growth in its exports.
India’s important export items include cotton, textiles, coffee, jute, tea, rice, wheat, mango pulp, jams, and vegetables. UK, Russia, Belgium, China, and USA are some of the countries that import goods from India.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
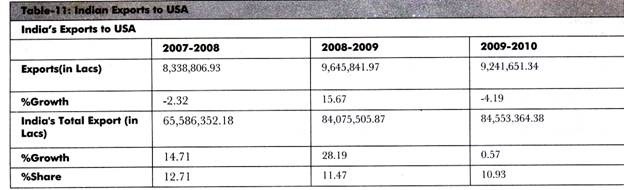
Table-11 shows the recent data of Indian exports to USA :( Source: Department of Commerce)
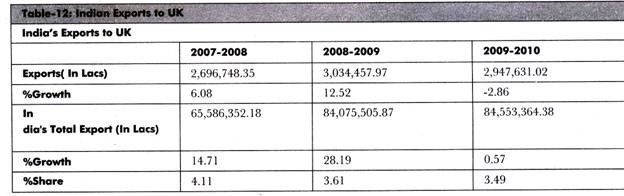
Table-12 shows the recent data of Indian exports to UK:
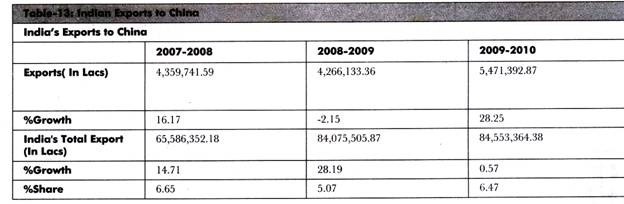
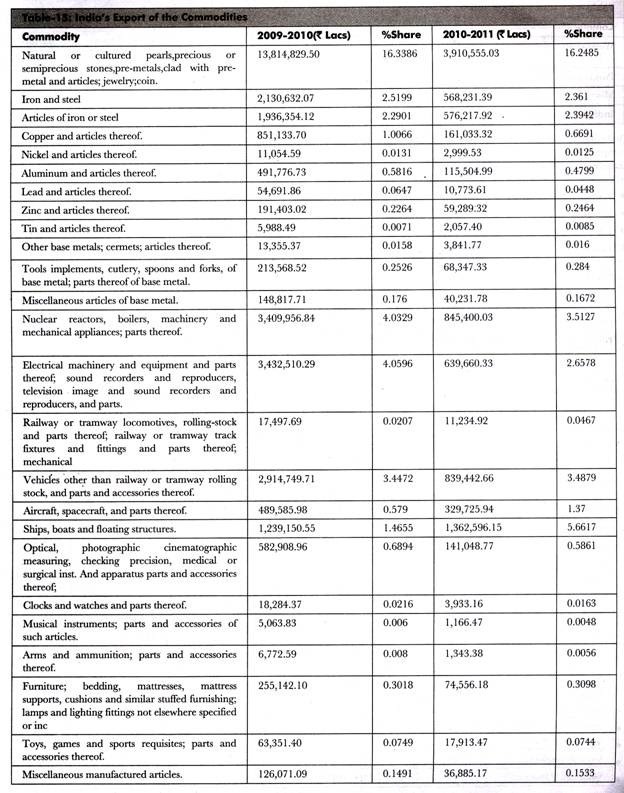
Table-13 shows the recent data of Indian exports to China:
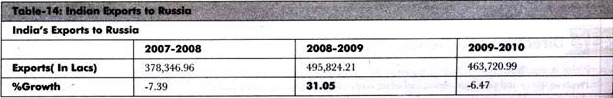
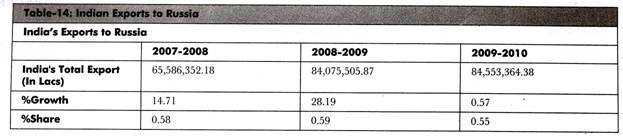
Table-14 shows the recent data of Indian exports to Russia:
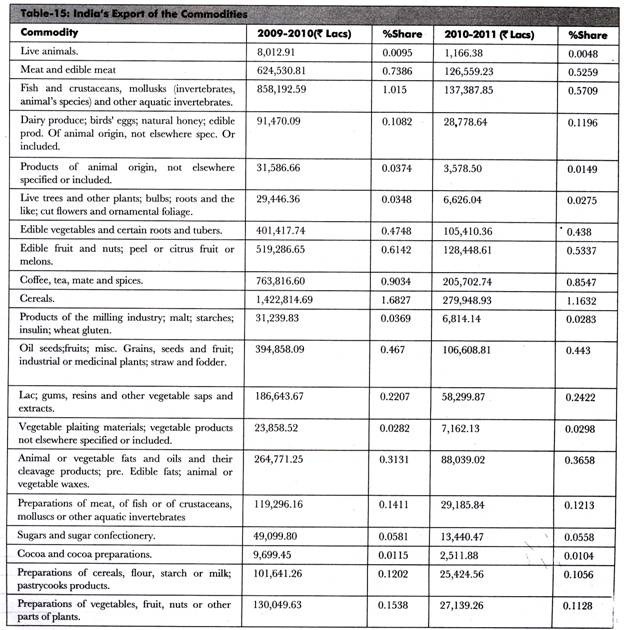
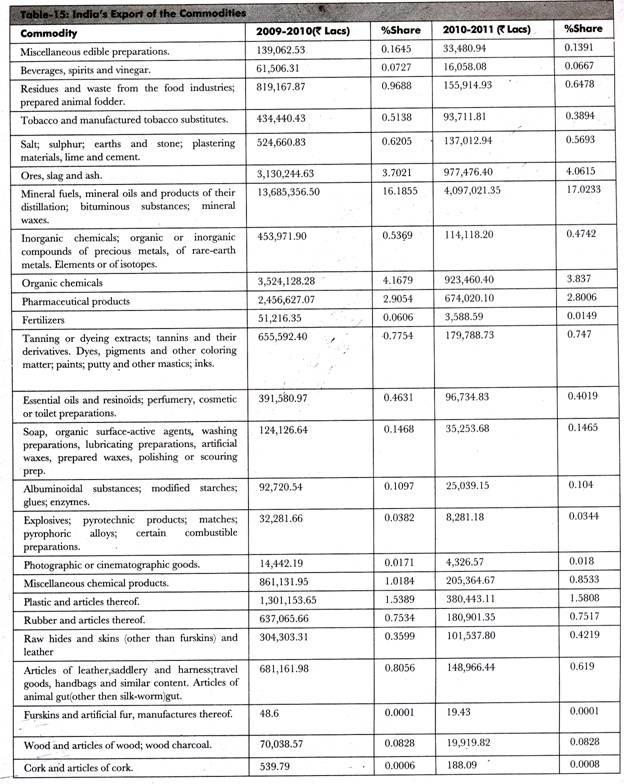
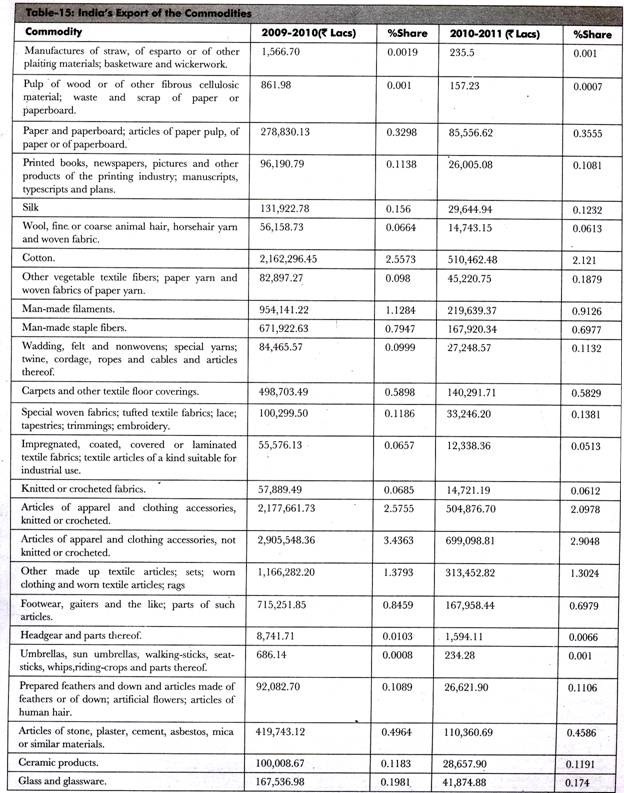
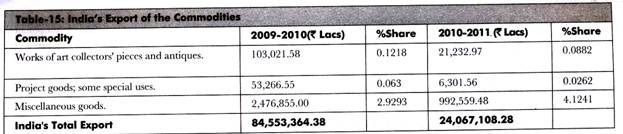
Table-15 shows the data of all the commodities exported from India to different countries in the year, 2010: (Source: Department of Commerce)
According to the survey (October 2010) done by Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), the competition in international market is increasing day-by-day.
The survey reports that the buying activities and payment conditions in international market are improving as compared to last year. This improvement in market conditions is influencing the exporters to build creative marketing strategies to gain profit.
Some of the efforts done by the exporters are as follows:
a. Appointing new distributors and maintaining relations with existing distributors
ADVERTISEMENTS:
b. Preparing aggressive advertisements in electronic media to attract customers
c. Arranging stock units in the target markets for smoother delivery and availability to the customers
It is important to note that the rising cost of raw materials negatively affects the exporters. In case of textile industries, the increasing price of cotton is causing anxiety among textile exporters. In addition, the fluctuating exchange rates may hamper the profits of exporters.
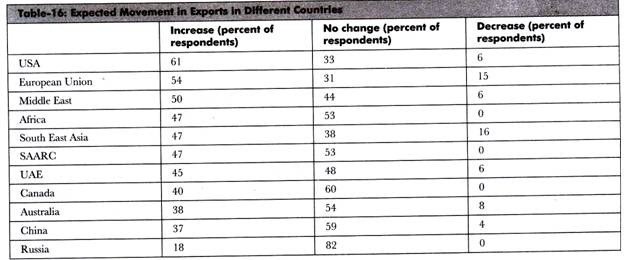
According to the FICCI survey, 64 % of organizations feel that export conditions are much better than the conditions six months back. The survey respondents were asked to tell their expectations of direction of exports that is whether the exports of different countries would increase/decrease or remain unchanged in coming years.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Table-16 depicts the result:
As shown in Table-16, respondents believe that the exports would rise in USA and Europe Union in coming years and fall in Russia. There are various factors that have a direct effect on international trade.
According to FICCI’s survey, some of the major factors that affect the Indian exports are as follows:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
a. Exchange rates
b. Rising cost of raw material
c. Weak demand in international market
d. Competitive environment
e. Increase in oil prices
f. Cost and availability of credit
ADVERTISEMENTS:
g. Inadequate infrastructure
h. Government procedures
i. Government promotional schemes
j. Tariff and non-tariff barriers
India has seen a positive change in its exports after liberalization. However, Indian exports have still not achieved its full potential. There still exists immense opportunities for expansion in exports.