The below mentioned article provides notes on National Highway Development Project of India.
India is lagging behind many countries of the world which built expressways capable of sustained speeds of over 100 kilometer per hour (kph). In recent years, a concerted effort has been undertaken, through new institutional arrangements and improved highway engineering, founded on a revenue model comprising, tolls and a cess on fuel, to build roads which deliver 80 kph sustained performance.
This project is known as National Highway Development Project (NHDP), the largest highway project ever undertaken by the country, is envisaged to convert 14,279 kilometers of national highway into 4/6 lanes at a total cost of Rs 65,000 crore.
National Highways Development Project (NHDP), was launched in 1999-2000 is promising to achieve a turn-around in the road sector hardly imaginable at the start of the Ninth Plan.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
NHDP comprises the 5846 km. long Golden Quadrilateral (GQ) connecting the four metros of Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata and the 7300 km. long North-South, East-West corridors connecting Srinagar-Kanyakumari and Silchar-Porbandar respectively 4/6 laning works on all but 700 km of GQ have been awarded.
GQ is expected to be completed by 2006 and the two corridors by 2008. NHDP also consists of Port Connectivity 380 km and other NH projects—962 kms. NHDP Phase III includes 4-Laning of 12,109 km of road undertaken under BOT in the year 2005 and to be completed by December 2009 at an estimated cost of Rs 80,626 crore.
Moreover, the Government has also proposed for two-laning with paved shoulder for 20,000 km of National Highways under NHDP Phase-IV and has also approved six-laning of 6,500 kms of national highways on October 5, 2006 comprising 5,700 kms of GQ and balance 800 km of other sections under NHDP Phase-V at a cost of Rs 41,210 crore.
Again Government approved construction of 1000 km of expressways on November 2, 2006 with full access control on new alignments at a cost of Rs 16,680 crore under NHDP-Phase VI.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The Government has also proposed construction of ring roads including improvement of NH links in city, grade separated intersections, flyovers, elevated highways, ROBs, underpasses and service roads at a cost of Rs 16,680 crore under NHDP-Phase VII.
Thus in order to give a boost to the economic development of the country, a massive programme of 4/6 laning of about 17,000 km of National Highways has been taken up since 1999 under the National Highway Development Project (NHDP) and is targeted to be completed by December 2009 at an estimated cost of Rs 76,000 crore.
This project is being implemented by National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), The NHDP has following eight components:
(i) Golden Quadrilateral (GQ):
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Comprising of the National Highways connecting four metro cities. This component has a total length of 5,846 km.
(ii) North South-East West Corridor:
Comprising the National Highways connecting Srinagar to Kanyakumari including Kochi-Salem Spur and East-West Corridor—comprising the National Highways connecting Silchar to Porbandar. These would cover a total length of about 7,142 kms.
(iii) Port Connectivity and Other NH Projects. 1,770 kms.
(iv) NHDP-Phase III:
4-Laning of 12,109 kms.
(v) NHDP-Phase IV:
2-laning of 20,000 km of NHs.
(vi) NHDP-Phase V:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Six-laning of 6,500 kms.
(vii) NHDP-Phase VI:
Construction of 1,000 kms of expressways.
(viii) NHDP-Phase VII:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
NH links in city, flyovers, ROBs, underpasses etc. of 700 km.
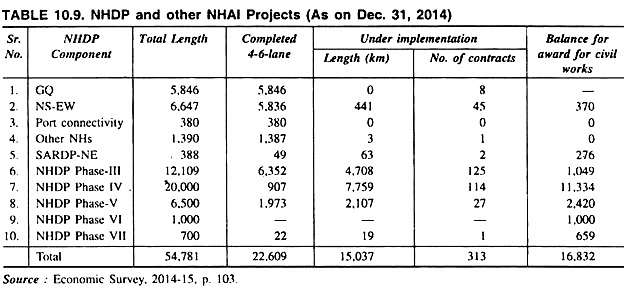
Table 10.9 shows details about the NHDP and NHAI Projects:
Table 10.9 reveals that 22,609 km of National Highways under NHDP projects have been completed as on December 31, 2014, the bulk of which 5,846 km lie on the GQ. In respect of North-South and East-West corridors (NS-EW), 5,836 km of 6,647 km is completed as on December 31, 2014.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
About 22,609 km of National Highways four-laning work is completed and 15,037 km work of National Highways is under construction. Nearly all work, on GQ has been completed by December 2012 and NS-EW corridors are expected to be completed by December 2015.
NHDP has been facing constraints in the timely completion of the project. These constraints include- delays in land acquisitions, removal of structures and shifting of utilities, law and order problem in some states and poor performance of some contractors.
Projects on road development have been taken up in various parts of the country with the assistance of World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB) and Japan Bank for International Co-operation (JBIC). With a view to further augment flow of funds to the sector, the Government announced several incentives for encouraging private sector participation in road development.
With the completion of more than 99 per cent of the GQ, a substantial impact upon the economy is already visible. At this stage, there is a need to focus attention on corridor management and road safety and NHAI has put in place a corridor management policy along with various safety measures in order to make the journey safe.
Under NHDP Phase-III, it is proposed to take up rehabilitation and upgradation of about 12,109 kilometers of existing national highways to 4-lane dual carriage way configurations under BOT basis.
The programme generally comprises stretches of national highways carrying high volume of traffic, connecting State Capitals with the NHDP Phase I and II network providing connectivity to places of economic, commercial and tourist importance.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Moreover, the Central Road Fund has been revamped by crediting a cess of Rs 1.50 per litre of petrol and diesel which is further revised to Rs 2.00 per litre in the Union Budget, 2005-06. In order to give statutory effect, a Central Road Fund Act, 2000 has been enacted in December 2000.
An amount of Rs 5,590 crore was allocated during 2000-01 under the revamped fund. Thus the financing of NHDP is based on funds from the Central Road Fund (CRF), multilateral financing agencies like World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB) and Japan Bank for International Co-operation (JBIC), market borrowing and private sector contribution.
Thus about 50,000 km of National Highway in the country are now being improved with an investment of Rs 2,20,000 crore which will boost economic growth.
Thus government’s ambitious 5,846 km. Golden Quadrilateral (GQ) is almost complete. The 6,647 km corridors linking Silchar and Porbandar and Srinagar and Kanyakumari will be completed by 2015. Improvement and widening of highways will reduce the requirement of fuel by 30 to 35 per cent, lessen travel time considerably and improve the durability of vehicles as a result.
In recent years, NHAI prepared plan to implement various road projects of about 50,000 km of which widening of about 21,000 km have already been completed. The NHAI has earmarked Rs 11,885 crore on the projects for the year 2013-14.
The total cost of about 50,000 km project is about Rs 2 lakh crore and about half of which has already been spent. The NHDP aims to construct 34,108 km in four phases and it has so for completed widening of 7,501 km while work is under way for 11,459 km. The balance 15,148 km are still to be awarded.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
However, the NHDP in facing the problem of slow progress of projects. The 7,142 km long NS-EW corridor which was originally scheduled to be completed in 2009 but the completion of the project was delayed due to problems in land acquisition and law and order in some parts.
Thus, the Road Transport and Highway Ministry has already taken the issue with the concerned state governments asking their cooperation for expediting the project for its final implementation.
Financial Position of NHAI:
NHAI collects most of its finance from cess funds, external assistance, borrowings and budgetary support from the Central Government. The funds collected from the cess are leveraged by NHAI to borrow additional funds from the domestic market.
The Government of India has also taken loans from the World Bank (US$ 1,965 million), Asian Development Bank (US$ 1,605 million) and the Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) (Yen 32,060 million) for financing the projects under NHDP.
These loans are passed on to NHAI by the Government partly in the form of grant and partly as loan. NHAI has also negotiated a direct loan of US$ 165 million from the ADB for one of its projects. The funds provided to NHAI including the borrowings from the market are utilised for the projects and for servicing and repayment of borrowings from the domestic market.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
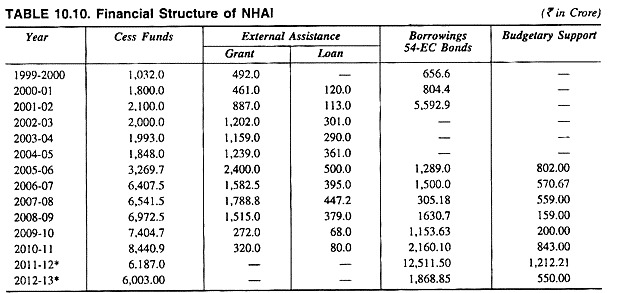
Funds received from the Government and funds borrowed by NHAI year-wise are given in Table 10.10.
Table 10.10 reveals financial structure of NHAI. NHAI received cess funds from Central Road Funds and the amount increased from Rs 1,032.0 crore in 1999-2000 to Rs 6,187.0 crore in 2011-12. The amount of grant received from external assistance also increased from Rs 492.0 crore in 1999-2000 to Rs 1788.8 crore in 2007-08.
Again the amount of loan received by NHAI from external assistance also increased from Rs 120.0 crore in 2000-01 to Rs 447.2 crore in 2007-08.
NHAI also borrowed varied amount from the market and the amount of borrowing varied from Rs 5,593 crore in 2001-02 to Rs 12,511.5 crore in 2011-12. Moreover, the budgetary support of the government to NHAI also varied from Rs 802 crore in 2005-06 to Rs 1,212.2 crore in 2011-12.
Thus it is found that the main source of finance of NHAI for its various NHDP projects is the fuel cess charged at the rate of Rs 2 per litre on both diesel and petrol and borrowings.