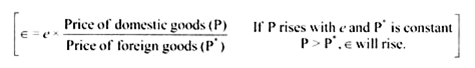I. Expansionary fiscal policy at home:
When Government increases the purchases or decreases tax, the national saving will decrease because National Saving = Y – C – G
S – I decreases, leading to a trade deficit.
Reason:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
When world interest rate remains constant. Investment does not change but due to an increase in Government expenditure, national saving (Y – C – G) decreases and thus NX falls leading to a trade deficit.
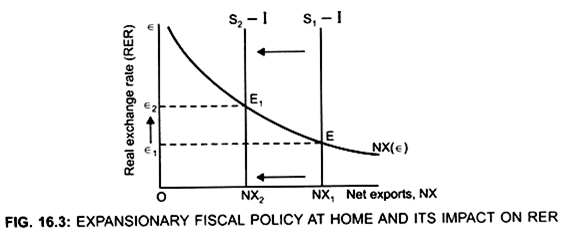
Initially the economy is in equilibrium where NX curve intersects initial S1 – I curve.
S1 -I = NX is at point E.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
... At point E: RER → є1
NX = 0 [NX = S – I]
There exists Balanced Trade
Due to expansionary fiscal policy national saving decreases.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
... S-I curve shifts to the left from S1 — I to S2 — I
It implies that, supply of dollars to be invested abroad decreases. Due to decrease in supply of dollars with demand for dollars remaining same, the RER rises from є1 to є2.
Equilibrium RER is є2.
Rise in RER means that value of dollar rises, that is, dollar becomes more valuable
Result:
Domestic goods become more expensive, relative to foreign goods. As a result Exports will fall, imports will rise, NX will fall and there will be trade deficit.
II. Fiscal policy abroad:
If the foreign Government increases Government purchases or cut taxes World saving will reduce
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Result:
world interest rate will rise, which reduces domestic investment (I) because investors will invest where they get high interest rate
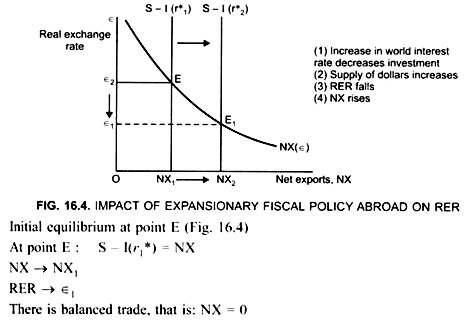
S – I in domestic country rises; thus, NX rises, leading to a trade surplus.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Increase in world interest rate from r1* to r2*, due to expansionary fiscal policy abroad, shifts the S -I curve to the right from S – I (r1*) to S – I (r2*)
World saving decreases because S = Y – C – G
Due to rise in world interest rate, investment at home will fall.
Result – supply of dollars to be invested abroad will increase and Equilibrium RER will fall from є1 to є2
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Since є = e x P/P*
Fall in RER means P* > P
This means domestic goods are less expensive relative to foreign goods. This will lead to a rise in demand of domestic goods in the world market. Our exports will, thus, increase. On the other hand, since foreign goods are expensive than domestic goods, demand of foreign goods in the home country will fall.
Result: EX > IM
NX will rise from NX, to NX2
NX will be positive and there is Trade surplus
ADVERTISEMENTS: