To begin with, it is important to understand what managerial economics is about?
Managerial economics is concerned with the application of economic theory and methods of decision sciences to analyse decision-making problems faced by business firms.
The first and most important problem faced by a business firm is the choice of a product to be produced or service to be provided. The second important problem dealt with in managerial economics is to decide by a firm about price and output of the product so as to maximise profits or to attain some other desired goal.
The decisions regarding these require careful analysis of the demand for its product and costs of its production. The other important decision-making problems facing business firms relate to what methods or techniques of production are to be used in the production of commodities, and how much advertisement expenditure is to be incurred for promoting the sales of their products. In deciding about all these problems, a firm has to decide how it can use its limited resources to achieve its objective most efficiently.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The science of economics is concerned with the allocation of scarce resources to alternative uses so as to achieve maximum possible satisfaction of the people. Thus, Lord Robins defines economics as a “Science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses”. The type of decision-making by managers of business firms also usually involves question of resource allocation within a firm or organisation.
The resources at the disposal of a firm are scarce or limited. What product to be produced, what price should be fixed, how much quantity of it should be produced, and what factor combination or production technique be used for the production of goods involve resource allocation by a firm. It is the task of a manager of a firm that it should take decisions regarding these resource allocation problems in a way that ensure most efficient use of resources. Only this will enable the firm to achieve the goal of maximisation of profits.
Thus, management science is concerned with the allocation of scarce resources at the disposable of the firm. While economics is primarily concerned with the allocation of scarce resources so as to achieve maximum social welfare management science deals particularly with organising and allocating a firm’s scarce resources so as to achieve the objective of the individual firm which generally happens to be maximisation of its profits. Therefore, management science’s is intimately related to economics.
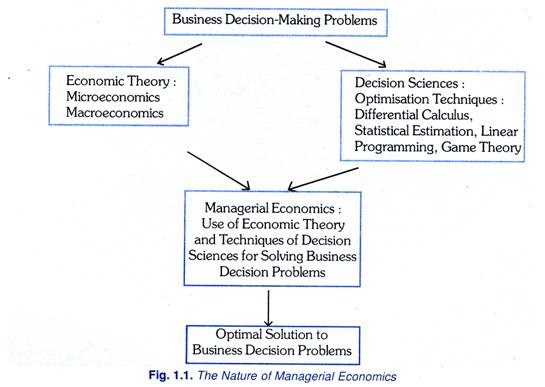
Besides economic theory, managerial economics draws heavily on the decisions sciences for the techniques used for decision making. The techniques of decision sciences used especially for business decision making are optimisation techniques, particularly differential calculus and mathematical programming. These optimisation techniques are used in the analysis of alternative courses of action and the evaluation of results obtained so that best alternative which helps in attaining the objective efficiently is chosen.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In addition to the optimisation techniques, methods of statistical estimation, game theory of decision sciences are extensively used in managerial economics for developing decision rules that can help managers in achieving firm’s objectives. It may however be noted that these techniques of decision sciences have now become a part of modern economic theory. Thus, the role of economics and decision sciences in managerial decision-making is illustrated in Figure 1.1. To conclude, managerial economics refers to the application of economic theory and methods of decision sciences to arrive at the optimal solution to the various decision-making problems faced by managers of business firms.
It is important to note that managerial economics has both descriptive and prescriptive roles. Managerial economics not only explains how various economic forces affect the working of a firm but also predicts the consequences of the decisions made by it. This is its positive or descriptive role. In addition to this, managerial economics prescribes the rules for the improvement of decision making by firms or their managers so that they can achieve their objectives efficiently. This is its prescriptive role.
It may be noted that managerial economics deals with not only private firms but also public enterprises. Further, the technique, approach or way of thinking of managerial economics can also be profitably used in non-profit making organisations such as colleges, universities. This is because managers of all types of organisations face similar problems. In the last about three decades managerial economics has grown rapidly because it has been increasingly realised that economic theory and its methods and concepts can be used by managers to efficiently achieve the desired objectives of the firm.
1. Managerial Economics and Economic Theory:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Managerial economics uses economic theory to solve business decision-making problems. Economic theory has been broadly divided into microeconomics and macroeconomics. Briefly, microeconomics deals with the theory of decision-making by individual consumers, resource owners and business firms in a free market economy. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, focuses on the study of economy as whole and its various aggregates such as national income, aggregate level of employment, general price level. It is important to note that though managerial economics draws on both microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Managerial economics is however essentially a course in applied microeconomics, macroeconomic conditions of the economy such as level of aggregate demand (which determines whether recessionary or boom conditions prevail in the economy), rate of inflation, rate of economic growth, that make up macroeconomic environment within which firms work are also very important for decision making by business firms.
Microeconomics has built models which explain how an individual consumer chooses among goods so as to maximise his satisfaction and individual business firm decides to fix price and output of its products to maximise profits and what factor combination it uses for producing them so as to minimise cost for a given level of output.
The parts of microeconomics which deal with demand theory, analysis of cost and production, theory of determination of price and output under different market structures are particularly useful in making business decisions about such matters.
The study of macroeconomics which focuses on the economy as a whole is also highly useful for management economist who is faced with various decision-making problems. This is because firms do not work in a vacuum. The level of overall economic activity, national income and employment, aggregate demand conditions, government policies (both fiscal and monetary), interest rate, the changes in price level greatly affect business firms.
These aggregates of the economy make up the macroeconomic environment which affects business decisions of managers. Therefore, in recent years macroeconomics for management which is particularly relevant for business decision making has been developed.
Forecasts of future demand, investment decisions by business firms are especially based on the overall situation of the economy and its growth prospects. Macro-theories of consumption, investment demand, the general price level and business cycles are particularly relevant for making capital investment expenditure which yields returns in future years.
2. Managerial Economics and Decision Sciences:
Managerial economics depends on economic theory for theoretical framework for analysing the problems of business decision-making. On the other hand, decision sciences provide tools and techniques for constructing decision models and for evaluating the effect and results of alternative courses of action (i.e., alternative business strategies). Business economics uses optimisation techniques including differential calculus, linear and other types of mathematical programming for deriving decision rules which assist managers for achieving the objectives of business firms.
Further statistical tools of the decision sciences are used to estimate the relationship between important variables which help in decision making. Besides, forecasting techniques of decision sciences are also widely used in business economics. Since most of business decisions require forecasting of future demand, and yield from capital investment, forecasting techniques play an important role in managerial decision-making.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Thus, business economics draws heavily on decision sciences.Optimisation techniques, statistical estimation, and forecasting methods have now become an integral part of modern economic theory.