Personal selling is a part of promotional- mix and it is an art of person-to-person communication for persuading prospects or consumers in the sales process.
For introducing effective marketing system, balancing of other marketing elements like, product development, pricing, distribution system, advertising etc. should be organised along with implementation of personal selling methodology.
“Personal selling is an ancient art. Effective sales persons have more than instinct; they are trained in a method of analysis and customer management. Selling today is a profession that involves mastering and applying a whole set of principles”. (P. Kotler).
Learn about:- 1. Definitions of Personal Selling 2. Meaning of Personal Selling 3. Objectives 4. Nature and Scope 5. Importance 6. Role 7. Evaluation of Personal Selling Efforts 8. Features 9. Functions 10. Process 11. Factors Determining the Kind of Selling Personnel 12. Difference between Advertising and Personal Selling 13. Advantages and Disadvantages.
Personal Selling: Definitions, Objectives, Nature, Scope, Importance, Functions, Advantages, Disadvantages and Features
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Contents:
- Definitions of Personal Selling
- Meaning of Personal Selling
- Objectives of Personal Selling
- Nature and Scope of Personal Selling
- Importance of Personal Selling
- Role of Personal Selling
- Evaluation of Personal Selling Efforts
- Features of Personal Selling
- Functions of Personal Selling
- Process of Personal Selling
- Factors Determining the Kind of Selling Personnel
- Difference between Advertising and Personal Selling
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Personal Selling
Personal Selling – Definitions: Provided by Eminent Authors Like P.Kotler, Carter & Whitehead, Daniel S. Warner, Pedeson & Wright, David J. Schwartz and a Few Others
“Personal selling is an ancient art. Effective sales persons have more than instinct; they are trained in a method of analysis and customer management. Selling today is a profession that involves mastering and applying a whole set of principles”. (P. Kotler).
Personal selling may assume different styles and all the styles may not be consistent with the marketing concept.
No sales approach works best in all circumstances.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Simply stated, salesmanship means selling techniques. But the term is now used with a sense of greater significance. To understand the meaning of salesmanship in the modern marketing context, we give a few definitions.
Salesmanship is not “an attempt to induce people to buy goods” but it is “the art of presenting an offering that the prospect appreciates the need for it and that a naturally satisfactory sale follows” (Carter & Whitehead).
“A face to face persuasive communication between a seller and a prospective buyer” (Daniel S. Warner).
Salesmanship is “the process whereby the seller ascertains and activates the needs or wants of the buyer and satisfies the needs or wants to the mutual continuous advantage of both the buyer and seller” (Pedeson & Wright).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Salesmanship is “the personal presentation of tangible or intangible products, including ideas of commercial significance to potential buyers” (David J. Schwartz).
“It is part of a salesman’s business to create demand by demonstrating that the need does exist, although before his visit there was no consciousness of that need” (W. Major Scott).
“Salesmanship consists of winning the buyer’s confidence for the seller’s house and goods thereby arising a regular and permanent customer” (G. Blake).
From the definitions given above, one common feature of salesmanship emerges; that common feature is – salesmanship is an activity involving satisfaction of both the buyer and the seller.
Salesmanship contains in it the idea of persuasion. What is actually needed by a man is to be sold to him – this is salesmanship. There must be a common point of view with the prospect in regard to the desirability of some article, service or idea. As a matter of fact, salesmanship is the act of ‘one human mind influencing another human mind’.
A salesman actually sells his point of view but the important point to note is that the salesman must start with the point of view of the prospect and leads his mind to the point where he will accept the salesman’s theory. The salesman, to be truly called a salesman, will not sell his goods or services but his ideas.
The old concept of salesmanship has, therefore, undergone changes. The art of selling is not salesmanship today; the art of knowing one’s mind and influencing it is salesmanship.’ To know your mind and then to let you know my mind and then to influence or persuade you to identify your mind with that of mine and when the two minds thus become identical, then selling of goods or services takes place. Before that, what goes on between the prospect and the salesman is the process of understanding each one’s mind’.
There is a term used in the marketing world — ‘aggressive salesmanship’ i.e., selling by pressurizing the customer. It has been found that this approach to salesmanship does not pay in the long run. The prospect cannot be made a permanent customer. Persuasion and not pressure, understanding and not commanding, patience and not intolerance, service and not extraction – are the key-notes of modern salesmanship.
Salesmanship is a matter of ‘give and take’; ‘give your prospect the service he needs, you will get from him the reward you expect’. On this maxim can a sound salesmanship exist and flourish.
Personal Selling – Meaning
Personal selling is a part of promotional- mix and it is an art of person-to-person communication for persuading prospects or consumers in the sales process. For introducing effective marketing system, balancing of other marketing elements like, product development, pricing, distribution system, advertising etc. should be organised along with implementation of personal selling methodology.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In modern marketing philosophy, a long term relationship and understanding with the consumer should be developed through consultative selling process. Personal selling helps consumers to realise the suitable benefits of the product and services offered to satisfy their needs.
A situation in which two people interact is known as “dyad”. In a ‘buyer-seller dyad’ the consumer shall have more opportunity to know about the sales person and the company. Through researches it was observed that the possibility of positive results are high when the characteristics and nature of the sales persons and prospects are alike. Sales persons’ behaviour shall influence the purchase process and satisfaction of the consumers.
To analyse the diversified personal selling situations, distinction should be made between service and developmental selling. Service selling is targeted to the existing customers whose behavioural and purchase pattern are already known to the sales people. For example, in the course of delivery of necessary products like, bread, milk, fuel or gas, the delivery person and the consumer are known to each other. The other form of personal selling is known as developmental selling.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Developmental selling shall aim at converting the prospects into customers. In this process, the people who do not currently view the company’s product or services favourably, and purchasing similar product from other sources, should be convinced and changed favourably.
It is the creative aspect of sales persons to offer the satisfactory services. Developmental selling may be organised for tangible products like, automobiles, vacuum cleaners, washing machines etc. and also for intangible products like, insurance, bank-schemes, advertising services etc.
Personal Selling – 14 Important Objectives
The objectives of Personal selling are as follows:
1. To enhance the sales volume of the different products of the company
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. To ensure the there is a proper mix of products in the total sales volume
3. To ensure that the market share of the company is increased
4. To ensure that the profits of the company have improved
5. To bring down or reduce the overall selling expenses of the company
6. To gain new accounts and ensure that there is growth of the business
7. It helps in the appointment of dealers and expansion of the distribution channel.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
8. To secure channel members co-operation in stocking as well as selling the products of the company.
9. To achieve the desired proportion of cash and credit sales.
10. To provide pre-sale and after-sale services.
11. To train the dealers and customers.
12. To assist and support other promotional measures.
13. To help in collecting the amounts due from the market.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
14. To help in gathering and reporting marketing intelligence.
Personal Selling – Nature and Scope
Personal selling is a tool and an integral part of the overall promotional programme. It should be oriented and designed with the variety of changing situations. Personal selling shall encompass different functional activities at various stages.
According to Thomas R. Wotruba there are five distinct stages of personal selling:
1. Provider Stage – In this stage the available offerings of the supplier are placed before the, buyer for the purpose of selling.
2. Persuader Stage – It is a process to peruse the selling process to the prospective market members.
3. Prospector Stage – In this stage the prospective buyer’s need is to be identified and the relevant goods and services offered as per requirement.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Problem-Solver, stage – In personal selling, sales person should act as the facilitator to solve the problems of the buyer in the specific area and should suggest the best solution through offerings, corresponding with the needs.
5. Procreator Stage – Buyer-seller interaction should generate an understanding, and offerings may be regenerated in a tailor-made fashion to match the specific need.
Role of personal selling is passing through rapid transition due to:
1. Availability of more information regarding the market.
2. Increasing of economic power in organised sectors,
3. Advancement of technological developments
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Enhancement of managerial efficiency.
5. Globalisation effect on the economy.
To combat all these forces and to compete with the challenging situation the marketers are developing different systematic approach in personal selling programme. In addition to the presentation of the offerings, sales persons should act as the information provider, influencer and demonstrator.
They should organise proper survey of the consumers’ specific need area. Accordingly the available products should be reorganised to suit the requirement of the prospect. Customers should be inspired and satisfied with the tangible values of the offerings with commitment of future support.
Responsibilities of personal selling may be categorised as follows:
1. Locating prospective customers.
2. Identifying customers’ needs and wants.
3. Counselling the prospects and suggesting, the possible solutions of the problems.
4. Securing and maintaining customers’ cooperation in promoting the product line.
5. Informing customers regarding the changes in the product line and other strategies.
6. Assisting customers by giving advice regarding technical aspects of the product.
7. Collecting and reporting of market information to the management.
8. Analysing the market potential.
9. Capturing and retaining a certain market share.
10. Demonstrating the organisational product and the special features.
11. Acquiring the prospect’s commitment and closing the sale.
12. Maintaining customers’ loyalty through follow up and after sales service.
Personal Selling – Importance
Promotional mix or the marketing communication-mix includes personal selling and non-personal selling (i.e., advertising, sales promotion and publicity).
Personal selling uses salesmanship technique which is the ability to influence prospective buyers to buy a good/service which otherwise they would not bring or postpone.
1. Personal selling is oral communication with potential buyers of a product/service with the intention of making a sale deal.
2. Personal selling is an important tool for meeting promotional objectives.
3. Personal selling occurs when an individual sales person sells a product, service or solution to a client.
4. No activity is more vital to the company’s health than personal selling.
5. Personal selling enables a person to confront new challenges almost every day.
6. For a sales person, every day is an adventure.
7. Working in selling profession one can go from the height of exhalation to the depths of discouragement within forty eight hours and climb back to the height again the next day. This is really exciting.
8. Importance to management- In this age of growing competition, sales person can effect large volume of sale and the margin of profit being small, the large sales volume will keep the firm profitable.
9. Importance to customer- Sales persons educate and guide customers, for product features and application which gives the customer more satisfaction.
10. Salesmanship is a creative approach and it can create needs and converts needs into wants.
Personal Selling – Role
The specific responsibility and role of personal selling in the promotional- mix should be chalked out carefully to avoid any unnecessary complications.
Personal selling programme should concentrate on the following issues:
1. Specific information to be exchanged between the organisation and the prospects.
2. Determination of different alternative means of communications for the purpose of fulfilling the objectives.
3. Estimation of the effectiveness of each alternative and its cost implication.
It is the role of personal selling to fulfil the communication objectives for the purpose of conveying various messages designed by the organisation.
The objectives of personal selling may be analysed as follows:
1. Creating awareness,
2. Demonstrating product benefits,
3. Answering queries,
4. Countering misconceptions
5. Unearthing the potential inner needs,
6. Pushing products through Channels,
7. Price negotiation between buyers and sellers.
Personal Selling – Evaluation of Personal Selling Efforts
Sales department or the promotional manager should be able to assess the effectiveness of personal selling programme, considering certain criteria as mentioned below:
1. Market Intelligence and Follow up Actions:
The sales force should be equipped with the ability to procure feedback information regarding market trends, competitive activities, reactions of the customers. Sales force should inform the existing and new customers, relevant information regarding various promotional activities.
2. Implementation Scheme of the Programme:
The sales effort should be judged and assessed on the basis of effective implementation made through different activities, like presentation schemes, demonstration schemes, customer relationship programme etc.
3. Achievement of Communication Objectives:
The effectiveness of the personal selling effort is judged by the attainment of the communication objectives and shies results. Sales efforts should consist of sales calls, selling expenses, customer service and sales related activities. Sales result may be judged through number of orders, volume of sales, profit margin and selling skills.
Personal Selling – 7 Main Features
The following features of personal selling may be enumerated as follows:
(i) Seller and buyers come in direct contact with one another,
(ii) It involves oral conversation between seller and buyers regarding quality, price, characteristics, use etc., of the product,
(iii) In personal selling, seller wants to convince the buyers about the goods and services which he want to sell,
(iv) It involves the sale of goods and services personally,
(v) It is most effective tool in increasing the sales.
(vi) It helps in providing much important information to the enterprise regarding market,
(vii) It is oldest method of sale of goods and services.
Personal Selling – 10 Important Functions
Some of the important functions of personal selling may be summed up as under:
(i) To sell the goods to new and old customers;
(ii) To demonstrate the goods before customers;
(iii) To remove the doubts and confusions of customers about products;
(iv) To provide after-sale-services to the customers;
(v) To instruct the customers for the use of product;
(vi) To advise the customers on certain matters;
(vii) To maintain the record of sales;
(viii)To prepare long-term and short-term marketing programmes;
(ix) To train new salesman;
(x) To solve the problems of selling force.
Personal Selling – Process
The process in retail selling begins from the moment the customer enters the store. The first step involves connecting with the customer and then sailing through different steps until the sale is successfully closed. Conservative processes have predefined greeting methods but an innovative and result oriented-method would be to naturally connect with the customer, gauge his/ her needs, present merchandise properly, handle objections, look for buying signals, conduct a trial close, suggest add-ons and then close the sale.
Process # 1. Connect with the Customer:
Go beyond the technique of smiling, making eye contact and small talk. The salesperson can’t connect with the consumer if he or she has a premeditated opening. A salesperson with a smooth automatic opening that has had a positive response in the past will have a hard time doing this. But to bring passion into the sale later on, even the most successful salespeople need to learn how to connect on a different level, and with a few more customers.
To achieve this, one must bring a bit of his/her personality to the sales floor. There’s no substitute for this genuine approach. The salesperson has to be humorous, sweet, shy or confident while interacting with customers. He/she should help the customer open up and be able to look for signs that would trigger the desire to buy.
Process # 2. Probe Needs Subtly:
By communicating freely with the customer and striking a harmonious note, the needs of the customers can be understood even if they are not spelt out clearly.
Process # 3. Presenting Merchandise:
The merchandise has to be presented properly without loss of time. The salesperson should initiate the trial of the product by the customer and give truthful opinions. As far as personal products are concerned, salespersons need to be subtle and allow for the kind of personal space that the customer needs while trying out such products.
Process # 4. Handling Objections and Indecision:
The customer’s doubts ought to be clarified by the salesperson to his/her satisfaction. Sometimes the price of a product may be compared with those of competitors; a clear rationale for the price needs to be given in such cases. Trade journals, product hangtags, information booklets can be referred to while handling objections, if the merchandise involves high involvement.
Process # 5. Recognize Buying Signals:
The salesperson must respond quickly to buying signals, which may come in the form of certain positive statements by the customer. This is the opportune time to ‘ask’ for the sale. Most of the time, salespeople fail to ‘ask’ for the sale and hence run the risk of losing it.
Process # 6. Trial Close and Add-ons:
The trial close follows the process of ‘asking’ for the sale and add-ons (complementary) for the merchandise selected by the customer.
The objectives of selling add-ons are as follows:
(i) Up-selling – Up-selling is the process of increasing the ticket size by offering a larger-value item, or an item of a larger size in the case of merchandise in a supermarket, say upgrading from 250ml to a 500ml.
(ii) Cross-selling – Cross-selling involves offering related merchandise, for instance, if one buys a cutting board, cross-selling would mean offering knives. Or if one buys a shirt, an accessory like cuff-links.
(iii)Suggestive selling – This involves salespersons making suggestions to customers on, say, the best offers in the store or the latest arrivals. It is the responsibility of the salesperson to suggest something, leaving the decision-making to the customer.
Process # 7. Closing the Sale:
The salesperson initiates the process of preparation of the cash memo for the customer and leads him or her to the cash counter for making payment. Closing the sale would also mean thanking the customer for the sale and for the opportunity to serve while extending an invitation to come again to the store.
Customer service is key in the entire sales process and salespersons must be trained thoroughly. If required, re-training should be done so that the role the salesperson plays in a retail organisation is fruitful.
Personal Selling – Factors Determining the Kind of Selling Personnel
One key decision on person selling strategy is that on the kind of sales personnel to employ. It requires consideration of the company’s qualitative personal selling objectives i.e., what contribution should be expected from those performing selling jobs towards the company’s long term overall objectives? What should be their duties and responsibilities of such individuals? How should their job performance be evaluated? The management must squarely face up to these problems when it decides the kind of Sales Personnel to employ.
It is clear and beyond doubt that each company’s individual requirements as to the kind of sales personnel are different because the qualitative personnel selling objectives of each company have some degree of distinctiveness. In addition, each company deals with a unique set of marketing factors, such as the strength and weaknesses of its products, the motivations and buying practices of its customers and prospects, its pricing strategy, the competitive setting (pure competition, monopolistic competition, Oligopolistic competition, etc.,) and the relative strengths and weaknesses of the competitors.
Moreover, different selling jobs require different levels of selling and non-selling abilities, training and technical and other knowledge.
In determining the kind of sales personnel best fitted to serve the company’s marketing needs, we must understand what we expect from them i.e., the job objectives, the duties and responsibilities, and performance measures. Each salesperson has different job even in the same company. Knowing the salesperson’s job means knowing the particular job for particular sales person. Knowing the particular job helps the management to fit the person to the job and job to the person.
The following factors are considered when making a decision on the kind of selling personnel to employ.
Such factors are:
1. Product market analysis;
2. Analysis of salesperson’s role in securing orders;
3. Choice of basic selling style.
Factor # 1. Product-Market Analysis:
No person is capable of selling all kinds of products to all kinds of customers. At one extreme, a salesperson sells single product to many kinds of customers. At the other extreme, a salesperson sells a wide line of products to a single kind of customers. Most salespeople sell some products to some kinds of customers. The selling job differs for each salesperson. The selling jobs may be categorized as (i) Product specialists, (ii) Market specialist, and (iii) Combinations of product and Market specialization.
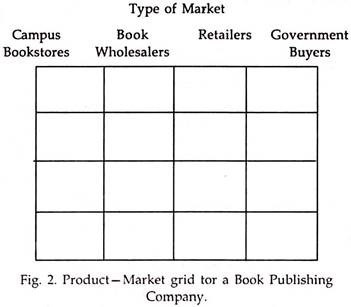
A critical step in sales job analysis is to define the product market interaction with the help of product market grid.
The grid demands a thorough analysis and classification of both of markets and products. The boxes in the above figure indicate the different customers who might be sold different products. As the management decides which products should be sold to which customers. The blacked in boxes indicate the management decision on which products should be sold to which customers. The result helps answer the question, should over salespersons be product specialist, market specialists or both.
Product specialization is needed when the product is highly technical and needs advice of the sales personnel on its uses and implications. Market specialization is called for ‘when the product is non-technical but different kinds of customers have unique buying problems, require special sales approaches or need special service. But in majority of cases, the sales personnel must have considerable knowledge of more than a single company product line and also in dealing with more than one kind of customers.
Determining the type and amount of specialization requires consideration of both the interdependence dimension and the expertise dimension. The four possible combinations of these two dimensions results in four different kinds of selling roles.
If the dominant interdependence is between customers (rather than between products), sales personnel should be specialists. They should be product specialists when the needed dominant expertise is in product technologies. They should be customer specialists when the needed dominant expertise is in customers’ applications. Customer specialist need the support of market managers’ who provide the necessary prospect expertise through their specialisation in applications in particular industries.
If the dominant interdependence is between products (rather than between customers), the selling organisation needs staffing by full live sales persons. If product technologies require the most expertise, sales persons sell the full live to all kinds of prospects and supported by product managers who provide the needed product expertise. If customers’ applications require the most expertise, salesperson sell the full live to particular kind of prospects.
In addition to product market interactions, other elements in a company’s market situation affect the caliber of salesperson required. The size of customers or the geographical locations has bearing on the type of sales persons. Different talents for instance, are required in case, the most customers are large than if most customers are small. Similarly geographic-locations also have bearing on the type of salesperson needed. For such or similar cases, appropriate grids assist in the analysis.
Factor # 2. Analysis of Salesperson’s Role in Securing Orders:
The second major factor in determining the kind of sales personnel is the analysis of role or roles in securing orders. The main objective of all salespeople is to seek orders. All salespeople seek orders aggressively in some situations but in others they take order coming their way, the relative emphasis or order taking and order getting varying in different selling environment.
The salesperson for a product which is popular in the market, is simply an order to take because the product is presold in the market whereas a salesperson trying to sell a product in the market and has to call on householders and customers most often function as order-getter, since getting orders is his main goal.
The salesperson’s role in securing orders also vary with the Promotional strategy relied upon. Depending on the Promotional strategy Personal selling or Advertising — sales people may be either active or passive forces in security orders. If the promotional strategy of the manufacturer is to rely heavily on advertising to attract business and build demand, marketing channels include several layers of middlemen and the role of salesperson is only passive and he acts only as order take and order getter only incidentally.
In the opposite situation where advertising is used only and mainly to back up personal selling, the sales person’s role is active and the salesperson’s role is that of order getter.
There are certain cases both in consumer goods and industrial goods marketing in which the salespeople play only a minor and indirect role in securing orders, the salesperson’s major role being concerned with certain other matters. In consumer goods marketing, the missionary salesperson’s major role is to assist middlemen in making sales to their customers. Orders from customers, then, will come via middlemen i.e., indirectly rather than directly.
In industrial goods marketing, such sales person (The sales engineer), plays two major roles – (i) Advising middlemen and the customers on technical product features and its applications, and (ii) providing design consultancy to middlemen and customers on installation or processes incorporating the manufacturer’s products. The salesperson, then, gets order indirectly through middlemen.
Factor # 3. Choice of Basic Selling Style:
The third important factor in determining the kind of selling personnel is the basic selling style as is being practised by the company. Actually, each company has differences in marketing factors and therefore, it requires a different kind of sales personnel that suits the company and can play a unique role even related to similar companies employing similar kind of sales personnel.
There are four basic selling styles generally in use i.e.:
i. Trade Selling,
ii. Missionary selling,
iii. Technical selling and
iv. New business selling.
i. Trade Selling:
The trade salesperson develops and maintains long term relations with a stable group of customers. This is low-key selling having little or no pressure and the job is rather dull and of routine nature. This selling style is generally used for product having well established markets and the role of salesperson is only to take orders.
In such cases, advertising and other forms of promotion are used as overall marketing strategy than is Personal selling. One important responsibility of the salesperson in this selling style is to help customers build up their volume through providing Promotional assistance. A trade salesperson most often devotes his time to promotional work with retailers and wholesalers.
ii. Missionary Selling:
The missionary salespersons do not sell to the end consumers. Their main objective is to increase the company’s sales volume by assisting customers (generally wholesalers or sole selling agents) with their selling efforts. Missionary salesperson do not often get direct, orders, since the orders obtained result from the missionary’s primary public relations and promotional efforts with customers of customers (indirect customers).
Thus, their main job is to persuade the company’s indirect customers to purchase goods from the direct customers. For example, a missionary salesperson of a drug manufacturing concern calls on retail druggists to acquaint them with the new product and to urge them to purchase the product with the company’s direct customers (i.e., wholesalers or sole selling agents) and to stock it. In some cases, missionary sales staff members call on individuals and institutions who do not buy the product themselves but influence its purchase by others.
For example, a representative from a drug manufacturer may call on doctors and hospitals to acquaint them with the new product in a thrust to get the product recommended to patients who will buy it from retailers (indirect customers). Missionary selling like trade selling is a low key selling and requires no technical knowledge.
iii. Technical Selling:
Technical salesperson is a technical hand and his main job objective is to increase company’s sales volume by providing technical assistance and advice to company’s established accounts. His main function is to advise just like missionary salesperson but in addition, sells direct to industrial users and other buyers. The technical salesperson devotes most of his time to acquainting industrial users with technical product features and its applications and to helping them design installation or processes that incorporates the company’s product. In this selling style, ability to identify, analyse and solve problems is important.
Technical salesperson often specialize either by products or by markets. In selling large made-to-order installations, such as, stream turbine or electric generators, they have to work with other technical personnel having specialisation in different items in the product line.
iv. New Business Selling:
The new business salesperson’s main job is to find out new customers or convert prospects into customers. Such salesperson are generally creative and ingenious and possess a high degree of resourcefulness. Few companies have salesperson whose main job is to get new business whereas in some other companies, regular trade sales person are expected to perform the job of new business salesperson also. However, these are two different jobs requiring, different talents and therefore, they generally ignore new business selling in favour of servicing their established accounts due to several reasons.
The company therefore, must choose the Selling style which suits its Selling Objectives.
Thus, the three basic factors as discussed above must be considered by a company when determined to consider the kind of Selling Personnel.
Personal Selling – Difference between Advertising and Personal Selling
Difference # Advertising:
1. Nature – Advertising offers a reason to buy.
2. Object – The object of advertising is to educate the customers to make the selling a success.
3. Control – The firm or advertiser has no control over the Medias (except mail advertising) as the media are controlled by media agencies.
4. Role – Advertising plays important role in the selling as it makes the way for personal selling.
5. Strategy – Its strategy is to attract the customer towards the product.
6. Relationship – It does not establish direct relationship with the present or prospective customers.
7. Differentiation – It does not differentiate the customers.
8. Tool – It is an important tool of marketing mix.
9. Personal or Impersonal – Advertising is impersonal communication of ideas.
10. Motivation – It gives information and educational motivation by impersonal methods, to buyers.
11. Attraction – Advertisements present facts and arguments to attract the customers.
12. Media – It can be presented through any media; vocal written or audio visual.
13. Anxiety – It creates anxiety to the customers towards the product.
14. Orientation – It is oriented largely towards the firm and its products.
15. Knowledge about effectiveness – It does not give the knowledge about the effectiveness on consumer psychology or behaviour.
Difference # Personal Selling:
1. Nature – Personal selling offers an incentive to buy.
2. Object – Its object is to solve the customer problems and increase the sales.
3. Control – Personal selling is fully controlled by the firm.
4. Role – Its role is to create interest and desires in the customers and then open the sales.
5. Strategy – Its strategy is to maximize sales, by taking the advantages of advertising and sales promotion.
6. Relationship – It establishes direct relationship with present and prospective customers, by personal contacts.
7. Differentiation – It differentiates the customers according to their level of incomes, culture, paying capacity, age, sex, etc.
8. Tool – It is an important tool of promotion mix.
9. Personal or Impersonal – It is personal communication of ideas.
10. Motivation – It gives personal motivation to the buyers who have been attracted by the advertisements.
11. Attraction – It gives encouragement, stimulation, motivation and solutions to problems to attract buyers.
12. Media – It can be presented through vocal media only.
13. Anxiety – It satisfies the anxiety through sales.
14. Orientation – It is consumer oriented.
15. Knowledge about effectiveness – It helps to understand the consumer psychology or behavior.
Personal Selling – Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of personal selling in comparison to other forms of communications may be expressed as follows:
1. Allowing more impact of the message – Two-way interaction between the sender and the receiver provides a direct approach to resolve any issue regarding the product and the message. In-depth discussion shall help to clarify any issue at the selling point.
2. Individual attention and clarification of the message possible – The messages may be clarified to the individuals for better perception and understanding.
3. Likelihood of distraction minimised – In case of personal selling/ the communication is made sender-to-receiver directly in one-to-one process. The possibility of distraction of the sales message is minimum in this form in comparison to other modes of communication.
4. Better problem solving possible – Personal selling process develops relationship marketing. Consultative selling process helps the buyer to identify the need and solve the problems through interactions.
5. Market potential can be analysed – Through in-depth discussion with the customers the potentiality of the market and possibility of gaining, market share can be ascertained from the field experience and research.
6. Instant feedback and corrective actions possible – Sales persons are directly in touch with the consumers and in a position to find out the reaction of customers regarding use value of the product and any suggestion for improvements Direct feedback from the customer shall help to undertake corrective measures for generating consumer satisfaction.
All the above positive aspects are not always realised. Personal selling programme developed in an unscientific and indiscriminate manner may create ill-effect and some practical problems.
The limitations of personal selling may be described as follows:
1. Communication objective if not standardised, may be distorted – In personal selling, the message objectives should be standardised and properly understood by the personal sales people. There is a possibility of alteration of, the messages by the sales person, and wrong methods of communication may affect the marketing objectives. In order to avoid these situations sales communication aid$ may be used to offset the problems.
2. Misunderstanding and misconception generated among the management and sales force may frustrate the personal selling programme – Good understanding between the marketing people and the sales people is essential for developing successful promotional programmes. Any internal conflict shall spoil the promotional objectives.
3. Cost of communication is high – In personal selling the post per sales is higher in comparison to other modes of communication system.
4. It cannot reach the masses – Personal selling is generally one-to-one communication. It can only reach to class pf people and not to the mass audience.
5. Sometimes sales force are beyond the control of the management – Sales personnel are directly handling with the clients in the process of personal selling. Their attitudes arid approach always cannot be controlled or monitored by the management. Some unethical approaches of the sales force may damage the image of the organisation.
In the integrated marketing communication system, personal selling programme should be used along with other forms of communications, like advertising, public relations sales promotion, direct marketing etc. Communication objectives can be better achieved if mass communication system like advertising programmes are effectively focussed before introducing personal selling.
Advertising shall be treated as appropriate medium for the purpose of creating awareness and conveying simple messages. For the purpose of analysing complex messages and for comprehending functional technicalities, demonstration through personal selling process shall generate better understanding. Personal selling also extends a cordial understanding to develop a relationship with the consumers to gain their confidence.