Read this term paper to learn about index number which is used to measure the changes in value of money.
Term Paper on Index Number
Term Paper Contents:
- Term Paper on the Meaning of Index Number
- Term Paper on the Types of Index Numbers
- Term Paper on the Procedure of Calculating the Index Number of Prices
- Term Paper on the Utility of Index Numbers
- Term Paper on the Limitations and Difficulties in Calculating Index Numbers
Term Paper # 1. Meaning of Index Number:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Value of money does not remain stable over a long period of time. It goes to changing as the price-level changes in the economy. The changes in the value of money are measured by constructing the Index numbers. The value of everything is measured in terms of money. But the value of money cannot be measured in terms of money. Money is generally wanted for the purpose of bringing goods and services.
Therefore, the value of money can be ascertained by averaging the prices of number of selected commodities on which people spend their income. The average of the prices of commodities and services on which a large chunk of money income is spent gives us the price-level and a series of such price level is known as the Index Numbers. In other words, the changes in the value of money can be measured only indirectly with the help of index numbers.
An index number is a device to measure changes in the level of any economic phenomenon. In a dynamic setting change occur very often and therefore, it is necessary to measure their direction and extent. It is likely that the prices may change over a period of time or even production and wages may undergo changes with the passage of time. All such changes can be measured with the help of Index Numbers.
Index number is essentially a mathematical device used to measure changes in the prices level. Index number of prices is a number representing the average price of selected group of commodities and services at a particular point of time. This number is always expressed comparatively i.e., in relation to the average price of the same group of commodities at some other time.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Even though it is possible to measure the value of money in relative terms, there are certain practical limitations. First, prices of all commodities and services do not rise uninformally. Second, people are not interested in the changes of prices of all commodities.
Term Paper # 2. Types of Index Numbers:
Different types of index numbers are as follows:
1. Retail prices index number.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Wholesale prices index number.
3. Working class cost of living index number.
4. General purpose index number.
5. Consumption goods index number.
1. Retail Prices Index Number:
The goods exchanged in the retail market and their prices are taken into consideration for constructing the index number of retail prices. Such type of index number shows the price movement in the retail market and their effect on the consumers. The essential for the construction of this type of index number is that the retail prices of the same goods and changes in them should be available accurately. The need for accurate statistics can hardly be exaggerated.
2. Wholesale Prices Index Number:
This type of index number is computed to measure the prices of commodities traded in the wholesale market. Since their general purpose index number is difficult to construct, the index number of wholesale prices is made use of as an index to measure the value of money in general. The goods transacted in the wholesale market and their prices are taken into consideration in constructing the index number of wholesale prices.
3. Working Class Cost of Living Index Number:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The goods and services consumed by the working class and their prices are taken into consideration while constructing the working class of living index number. This index number obviously shows the value of goods and services consumed by the working class. The working class cost of living index number reflects the cost of living of workers.
In a well-developed industrialised economy, this type of index number plays a very significant role as the demand for higher wages by the industrial workers depends upon their cost of living. Indirectly this index throws light on the consumption standards of the people.
4. General Purpose Index Number:
Such type of index number is constructed to measure the general price-level and through it the general purchasing power of money. The construction of this type of an index number is rather difficult and cumbersome as it includes the prices of almost all commodities produced in the country. The difficulty overcame in the U.S.A. by combining 12 different index numbers to construct the general purpose index number. Many experts consider this type of index number as hotch-potch as it includes the prices of all commodities produced in country.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
5. Consumption Goods Index Number:
This type of index number is of much importance to the consumers as it reflects the change in the price-level of the consumption goods. For the construction of this type of index number, the goods consumed by the people in general and their prices are taken into consideration. The statistician has to be very careful in selecting the commodities and giving them adequate weightage or importance.
Term Paper # 3. Procedure of Calculating the Index Number of Prices:
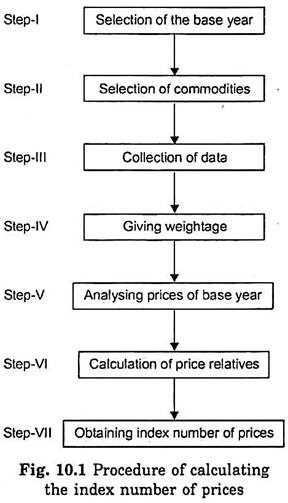
The index number is a device by which the changes in prices in different months or years are calculated and compared. To calculate the index number of prices, the following procedure is adopted in Fig. 10.1.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Step I:
Selection of the Base Year:
The number of prices index number of prices is meant to help us study the changes in prices between two periods. Hence, we should start from a particular year; this is the starting point or the base year. The base year should be a normal year and should be prominent in some respects. For instance, the choice of 1950- 51 was a suitable year to study the changes in prices and changes in the value of money after the first five year plan was introduced. Subsequently, 1960-61, 1970-71, 1980-81 and 1990-91 were chosen as base year for measuring price changes.
Step II:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Selection of Commodities:
The prices of all the important goods which are bought and sold should be included. Actually, it would be ideal to include all prices but this is not possible.
Step III:
Collection of Data:
Prices collected should be accurate, comparable, representative and adequate. Wholesale prices from big markets will be useful for as they will be accurate. But retail prices will have to be collected if index number is to be calculated to measure changes in the prices of consumer’s goods.
Step IV:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Giving Weightage:
All commodities which are included in an index number are not of equal importance. Some commodities, say wheat or rice are far more important than cigarettes. Hence, in the calculation of index numbers, weightage is given i.e., emphasis is laid on more important goods.
Step V:
Analysing Prices of Base Year:
After the collection of data, we must average the prices. By averaging we mean driving a simple arithmetic average for the base year. This requires reducing all prices in the base year to a common denominator 100. This is to be done because the subsequent variations could be expressed in terms of a percentage change in relation to the price of the base year.
Step-VI:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
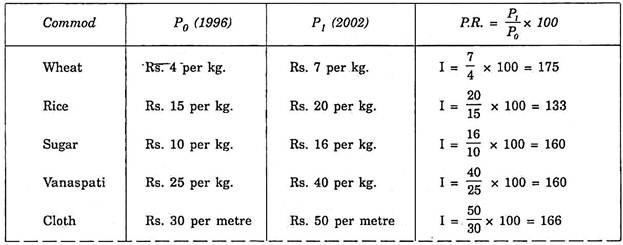
Calculation of Price Relatives:
The next step is to calculate the price relatives of each commodity taken into account. Price relative is a percentage variation in the price of a commodity in relation to the price of the commodity in the base year.
This is calculated as:
Step VII:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Obtaining Index Number of Prices:
Lastly add up price relatives and divide the sum total of price relatives by the total number of commodities taken into account to obtain the index number of prices.
Algebraically,
Index number of the current year = ΣI/N
Where Σ (sigma) implies the sum of:
I stands for price relatives; and
N denotes the number of commodities.
Illustration:
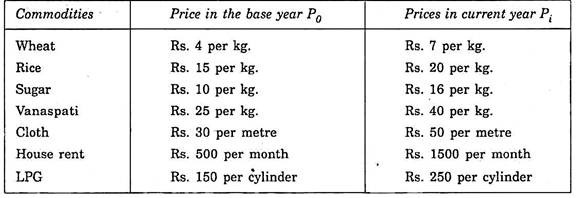
Let us take 1996 as the base year and 2002 as the current year.
The prices of different commodities in the base year and current year are as follows:
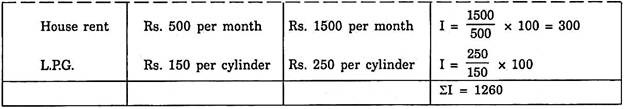
With this information, index number can be calculated:
Index Number = ΣI/N = 1260/7 = 180
Here, the index number is 180 in 2002 in comparison to 100 in 1996 (base year). It shows that there is nearly two times increase in the price level. It means that there is a fall in the value of money. The fall in the value of money is to the extent prices have raised. In 2002 approximately the value of money is 1/2 of what it was in 1996.
Term Paper # 4. Utility of Index Numbers:
The benefits of using index number in calculating the value of money are as follows:
1. We can measure any quantitative change in addition to changes in the value of money and the cost of living. There may be index numbers of wages, imports-exports, industrial activity, employment, change in areas under cultivation, change in population, etc. These measurements indicate social and economic trends and help in forming policies with respect to them.
2. Index number of wholesale prices can guide the currency authority not only in stabilising price levels but also in stabilising foreign exchange.
3. We can compare, with the help of index numbers, economic conditions of a class of people at two different periods.
4. Index numbers can also be used to compare the purchasing power of two currencies and to fix the purchasing power parity.
5. Index numbers can be used as a basis for an equitable discharge of contracts i.e., borrowing and lending. When prices rise, the creditor is a loser, for the same amount returned to him has less purchasing power. It should be more just to ensure that the creditor gets back the same purchasing power.
If that is so, then the amount of the principal should be increased in proportion to the increase in prices. Similarly, when the prices fall, the debtor should be asked to pay correspondingly less, otherwise the burden of the debt in terms of commodities and services will be increased in proportion to the fall in prices.
6. The method of index numbers is used for measuring changes in the price-level. This is essential for maintaining price stability. Price stability is conducive to the maintenance of economic activity at the desired level.
7. An index number of cost of living can guide us in the adjustment of wages to changing price.
Term Paper # 5. Limitations and Difficulties in Calculating Index Numbers:
Although index numbers provide a fairly broad guidelines to devise suitable policies of economic welfare and development, but it is not possible to measure accurately the changes in the value of the money due to following limitations:
1. The introduction of new goals which may act as close substitutes for old and high priced commodities cannot be taken into consideration.
2. The selection of weights is arbitrary and based upon the personal inclination of the statistician.
3. Changes in the quality of commodities and services cannot be taken into consideration.
4. The index numbers of different places are hardly comparable because the significance of prices to consumption varies according to task, habits, climates and such other factors.
5. The uniformity of basis necessary for comparison between different years may not always exist. Hence, it is difficult to draw any inference by comparing index number by a long period of time.