Read this article to learn about the top nine frequently asked questions on Basic Problems of an Economy and Price Mechanism.
Q.1. Why do Economic Problems Arise?
Ans. Human wants are unlimited and are insatiable. But the resources needed to satisfy wants are really scarce.
Thus, the scarcity of resources gives rise to fundamental economic problems of a nation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.2. What are the Central Economic Problems of an Economy?
Ans. Every economic system, regardless of its type, faces three fundamental economic problems.
These are;
(i) What goods and services are to be produced and in what quantities?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) How are these goods to be produced?
(iii) For whom are these goods to be produced?
Q.3. What do you Mean by the Problem of ‘Resource Allocation’?
Ans. Scarcity and choice are intimately related to each other. As resources are scarce, choice is inevitable. One of the major economic problems faced by any economy is what goods and services are to be produced. Obviously, limited resources are to be allocated among alternative uses in such a manner that all wants can be met. This is the problem of picking and choosing from the unlimited wants.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.4. What is a Production-Possibility Curve?
Ans. With given resources and technology, a production-possibility curve depicts the maximum obtainable combinations of two commodities that an economy can produce at the full employment level.
Q.5. Explain the Shape of a Production-Possibility Curve.
Ans. A production-possibility curve is concave form below or a bowed-out curve because of the operation of the law of diminishing returns to a variable input or law of increasing costs.
Q.6. How does Price Mechanism Operate in a Capitalist Economy?
Ans. In a free enterprise capitalist economy, the price mechanism, i.e., the free market forces of demand and supply, help to solve the fundamental economic problems of an economy. Price system indicates what goods and services should be produced. Secondly, how goods are to be produced can be learnt from the price system. Thirdly, prices play a role in the distribution of goods and services among the members of the society.
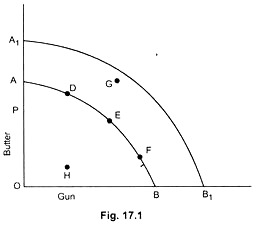
Q.7. In the following figure, we measure gun on the horizontal axis and butter on the vertical axis. Answer the following questions with the help of the production-possibility frontier AB.
(i) At which point on the curve AB a country will operate if it decides to produce only gun or only butter?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) What is the economic significance if a nation stays at point H and at point G?
(iii) What sort of effect an economy might experience if it contemplates to move from point D to E and from E to F along the curve AB?
(iv) How will the curve AB shift if economic development takes place?
Ans. (i) If a nation decides to produce only gun, it will operate at point B on the curve AB. Oppositely, if only butter is manufactured, the country will stay at point A on the AB curve.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) Operation inside the production possibility frontier, such as point H, implies that the available resources are not being fully employed and/or inefficiently utilised. On the other hand, operation outside the AB curve such as point G, merely suggests that the economy is incapable of producing more of both the commodities with its given resources.
(iii) If a nation moves from point D to E and to F along the curve AB, it will sacrifice butter for gun production. Gun output will increase since resources are now being constantly transferred from butter industry to gun industry. Hence, the reallocation of resources.
(iv) A production-possibility curve will shift rightward if economic development occurs. The curve A1B1 is the result of economic development indicating larger quantities of both commodities.
Q.8. What is Microeconomics?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Ans. Microeconomics or price theory studies and analyses the economic activities of individual economic units, such as a consumer, a producer and an input owner. Primarily, this branch of economics is concerned with the determination of prices of a product and an input.
Q.9. What is Meant by Price Mechanism?
Ans. Price mechanism is one in which all economic decisions are taken through the medium of prices which are, by nature, self-adjusting and self-correcting. Decisions of production, consumption and distribution are taken by invisible hand or the price system. Prices act as communicating or interacting devices.