This article will guide you about how to derive market demand curve.
Although the behaviour of an individual in respect of selection and purchase of goods forms the basis of demand theory, the aggregate demand or market demand for a good is most important for its producer.
The aggregate quantity of a good that the buyers purchase or demand at a particular price and in a particular period (e.g., in a day) is called the market demand for the good at the said price. Also, the curve that gives us the market demand for a good at any particular price is known as its market demand curve.
It is obvious from the definition of market demand that the horizontal or lateral summation of the individual demand curves for a good would give us its market demand curve. The market demand curve for a good would slope downward towards right, since, owing to the law of demand, the individual demand curves slope, in general, downward towards right (barring exceptions here and there).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
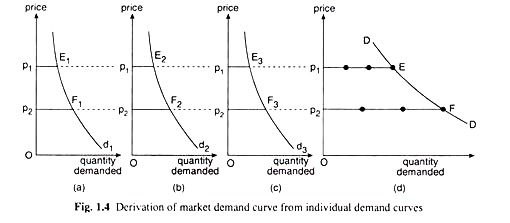
The market demand curve can be obtained from the individual demand curves with the help of Fig. 1.4. To make our analysis simple, suppose that the number of buyers of a good is only three, and their individual demand curves are respectively d1 d2 and d3 in Fig. 1.4.
From these three individual demand curves that at the price of p1, the individual demands of the buyers are obtained as p1E1, p1E2 and p1E3 respectively.
Here at p = p1 the market demand for the product is p1E1 + p1E2 + p1E3 = p1E [in Fig. 1.4(d)]. Therefore, the point E in Fig. 1.4(d) lies on the market demand curve for the product. Again, at p = p2, the individual demands of the buyers are respectively p2F1 p2F2 and p2F3. Therefore, at p = p2 the market demand for the product would be p2F1 + p2F2 + p2F3 = p2F [in Fig. 1.4(d)].
Therefore, the point F in Fig. 1.4(d) is another point on the market demand curve for the product. Many more points are obtained like E and F on the market demand curve for the product in the process’. Now join these points by a curve in Fig. 1.4(d), the market demand curve for the product is obtained. In Fig. 1.4(d), this curve has been obtained to be DD.
It is obvious from the method of obtaining the market demand curve that the market demand curve for a good is the horizontal summation of its individual demand curves.
Remember here that if the law of demand is effective for most of the buyers of a good, i.e., if most of the individual demand curves slope downward towards right, then their lateral summation, i.e., the market demand curve, would also slope downward towards right. That is, the law of demand is always effective in the case of market demand for a good.