In this article we will discuss about the physical and practical ideas of physiocrats.
Physical Ideas of Physiocrats:
The Physiocrats contributed on the theoretical side, three important ideas, namely:
1. The concept of natural order.
2. The concept of net product.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. The circulation of wealth.
1. Natural Order:
The physiocrats had firm faith in the philosophy of natural order. Nemours called Physiocracy as “The science of natural order”. Gide and Rist said “The essence of physiocratic system lay in their contribution of natural order”.
Natural order has been defined by the physiocrats as the providential order made by God for the welfare of mankind. It is universal and unchangeable. The natural laws are the expression of the will of God. To discover and to understand these laws is man’s first duty and to live according to them is his second duty.
According to the physiocrats the natural order is an ideal order given by God. It is different from the positive order made by men. In other words, the society which is governed by the laws of nature is an ideal society and the society which is ruled by positive laws made by the Government is an imperfect society.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The moral and religious philosophy is reflected in their concept of Natural Order. Natural order will increase the happiness of mankind. “Divine in its origin it was universal in its scope”. In short, the natural order is the best and most advantageous order for the physiocrats.
The physiocratic natural order had 3 important features:
1. Natural order aimed at securing pleasure to the people.
2. It aimed to increase the rights of the people without imposing any restrictions on their liberty.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. It stands against mercantilism.
The physiocrats believed that natural order maintained equilibrium in nature. The concept of natural order produced certain important practical results. It implied that only under conditions of freedom, man can enjoy the maximum happiness and derive maximum advantage in economic matters.
There should be minimum interference in economic affairs by Government. In other words, the physiocrats advocated laissez faire policy. The physiocrats believed that the individual interests were identical with the interest of the society.
Criticisms:
Physiocratic idea about natural order was vague and not clear. It was not the result of observation of external facts. It ignored the fact that the interest of the individual is not always in harmony with those of the society and “the individual is not always the best judge of his own interest.
2. Net Product:
The physiocratic concept of net product was the outcome of their nature philosophy. Physiocrats held agriculture supreme among all occupations, since it was the source of wealth. It is in agriculture that nature works along with man.
In the doctrine of net product the physiocrats introduced the fundamental idea of economic surplus. In the physiocratic system, agriculture has been given a dominant place because of its important role in the economic development of a country. Agriculture is the only sector which yields net product or surplus produce.
In other words it is only in agriculture the net wealth produced is greater than the wealth consumed. Net product is defined as the excess of wealth produced over and above what is required. The physiocrats introduced the idea of surplus resulting from the bounty of nature which they called “Product – Net” or “Net Product”.
Commerce and industry according to the physiocrats are the branches of agriculture because agriculture supports them by furnishing the necessary materials. The size of the net product shows the welfare of the community. Because of this fact the physiocrats advocated a light tax on agriculture. Net Product is the real revenue of the nation, a source from which manufacturing and commercial classes get their living.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
No other sector except agriculture is capable of yielding net product. In commerce the already produced commodities are transferred from one hand to another and nothing new is produced. In industry also the raw materials are modified and no surplus is produced.
In industry and commerce the wealth produced exactly equals to the wealth consumed. Thus industry and commerce are regarded as unproductive. Thus, Prof. Haney considers “The idea of Net Product was important for the development of economic analysis. From this developed, the idea of surplus which was to play an important part in later theories”.
3. The Circulation of Wealth: (Tableau Economique):
After having discovered the source of wealth, the physiocrats turned to the problem of how wealth produced by the agriculturists gets circulated among the different classes of the society. The physiocrats must be credited with being the first school of economists who analysed the problem of distribution.
The idea was first given by a famous physiocrat Quesnay through tableau economique. How much importance the physiocrats attached to the circulation of wealth is evident from what Turgot said the “it constituted the very life of the body politic, just as the circulation of blood did of the physical”.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
As Hector Denis said, “the discovery of the circulation of wealth in economic society occupied in the history of science the same position as is occupied by the discovery of circulation of blood in the history of Biology.”
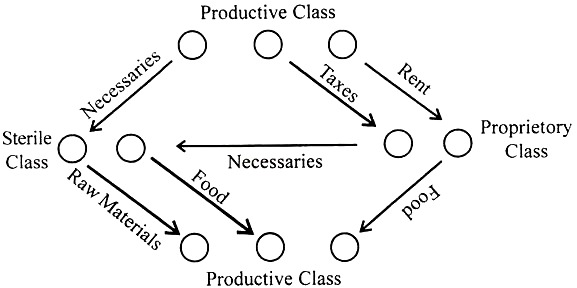
The most important contribution of physiocracy is the tableau economique. The author of this table was Quesnay. He was a doctor and so he applied his biological knowledge to the economy and compared the circulation of wealth with circulation of blood. The economic table represents the way in which circulation of wealth takes place in the economy. In his table, Quesnay has divided the society into three classes.
In other words the physiocratic system is based on the division of society into the following three classes:
1. The productive class. It consisted of farmers, who cultivate the soil and pay the rent to the landlords.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. The proprietary class included the landlords and the king.
3. The sterile class or unproductive class. This class included all those people who are engaged in non-agricultural occupations. Merchants, artisans, domestic servants, government servants, doctors, lawyers, teachers, etc. formed part of this class. It must be remembered that the physiocrats did not consider the sterile class as useless. It was unproductive in the sense that it did not produce any net product.
Among the three classes the farmers alone are the productive class because soil is the only source of wealth. After classifying the society into three classes, Quesnay traced the circulation of wealth among the three classes of the society in the following manner.
All wealth is produced by the productive class. The value of the total produce produced by the farmers in any year is equal to five million francs. Out of this agricultural class requires two million francs for their maintenance. So the two million do not circulate in the economy. The remaining produce worth of three million francs is distributed in the following manner.
Since the productive class requires industrial goods, it will buy them from the sterile class for one million franc, the remaining two million francs pass on to the hands of landlords and the government in the form of rent and taxes. The proprietary class lives on these two million francs. It spends one million francs for food and the other for the purchase of industrial goods.
According to the physiocrats the sterile class or unproductive class produces no surplus. But still it receives two million francs. The sterile class uses the two million francs for buying the necessaries of life and raw materials for industries from the productive class.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Thus the two million which have come into the hands of the unproductive class return to their starting point, namely, the farmers. Thus the cycle is complete.
The following figure clearly shows the circulation of wealth among the three classes of people:
The tableau economique is based on the existence of a social structure; land is owned by the landlords but cultivated by the farmers who became the productive class. The net product or surplus produced by the productive class is used for the satisfaction of sterile and proprietary classes. The tableau economique assumes constant prices for the commodities. Further, it assumes that the harvest is 100 percent and the expenses of the productive and unproductive classes are equal.
In short the tableau economique explains two things:
(a) How the net product circulates among the three classes?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) How it is re-produced each year?
Criticism of tableau economique:
Many complexities are involved in the circulation of wealth in a society. Today, one may be surprised to find that under the “Tableau”, the class which enjoys two-fifths of the national income does nothing in return first. The reason lies in the great reverence the physiocrats had for the land owners. The adjective “Sterile” is applied not to them but to the manufacturers and artisans.
Property is the foundation of the “natural order”. One might have expected that the premier position should have been given to the class which they turned productive i.e. the tillers of the soil. But the Physiocrats put proprietors above these tillers of the soil, because God, according to them, had willed that the farmers should be the first dispensers of all wealth. This idea was, undoubtedly, a great mistake on the part of the Physiocrats.
Another mistake was their failure to realise the inherent dignity of all true labour simply because it was not the creator of wealth. In the eyes of the Physiocrats, it was the nature that produced wealth and not the worker.
Hence, an industrial worker is unproductive whereas an agricultural worker is not. Since the Physiocrats lived in a feudal society, they suffered from an illusion as to the necessity for landed property similar to that which led Aristotle to defend the institution of slavery.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Its Importance:
Growth models:
There is one more advantage from the Tableau Economique. It can help us to understand and construct models. Some fundamental truths of interdependence of various sectors is revealed by it. It also shows that a number of conditions will have to be fulfilled for an overall balance. How the expenditure behaviour of one sector determines the constraints upon other sectors is also shown by this Tableau.
In the growth models, these very ideas are used. Input requirements and output supplies are worked out or assumed for different sectors. And in conjunction with other assumptions, conditions of the overall economic balance of stability are also worked out.
There is no denying the fact that modern growth models are much more complex. They consider the depreciation factors, time lags, gestation periods, changing supply position of various resources, technological changes, and demand changes and so on. Today’s models work out conditions of stability and instability in the economy.
At that time, when the tableau economique was published it was regarded as one of the greatest achievements of human mind. Gide and Rist are of the opinion that “Physiocrats were the first to attempt a synthesis of distribution and production. They were anxious to know how wealth passed from one class to another”.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Quesnay’s economique table is considered as the most important contribution of physiocracy. It is regarded as a pioneering attempt at national income analysis and mathematical economics. Quesnay was interested in the statistical data and tried to estimate the value of annual output. Quesnay’s net product is equal to that of Karl Marx’s surplus value.
Practical Ideas of Physiocrats:
The physiocrats did not analyse the problem of value in a systematic manner. They were interested only in production. According to them, value is connected with the usefulness of the commodity. They did not differentiate between value and price. Quesnay said “What is called value is price”. Value was not fixed but changed from time to time depending upon the demand.
1. Interest:
As for as interest is concerned physiocrats made a difference between money and capital. In their view capital is the result of saving and so interest on capital is justified. The physiocrats allowed interest charging for the loans which were taken for agricultural purposes because such loans were productive.
2. Population:
Physiocrats encouraged large population because they believed that large population increases consumption which results in an increase in production and so wealth will increase.
3. Taxation:
The physiocratic theory of taxation is connected with net product. They believed that only land produced a surplus, taxes should be paid from the surplus or net product. In short, they advocated a single tax system on agriculture. But an objection was raised against the single tax system because the government’s revenue will be less. Further, this type of taxation was not justified because it ignored the other sources of wealth to the government.
4. Private Property:
The physiocrats were believers in the institution of private property. The physiocrats regarded property as a tree and its branches are social institutions. In support of private property they stated that the landlords must enjoy 2/5 of the surplus because they are responsible for making land fit for cultivation. It is the landlord who provides the farmer the necessary funds for cultivation.
So, if the landlords are not given their due share, they will take away the land from cultivation. At the same time, the physiocrats imposed certain duties upon the landlords. They should bring new lands under cultivation and help and protect the farmers.
5. Trade:
The physiocrats thought that exchange was unproductive. Accordingly, industry and commerce were considered unproductive. So foreign trade which had assumed so much importance under mercantilism started losing its importance. The physiocrats thought that foreign trade produced no real wealth. So some of the physiocrats even considered foreign trade as an evil.
However, the physiocrats were not entirely against foreign trade. They believed that a country should exchange only those goods which it cannot produce and those which are in excess of consumption. As a result, the physiocrats advocated free trade.
6. Functions of State:
In the natural order of Physiocrats, the functions of the state would be reduced to the minimum, i.e., to protect the country and the life, liberty and property of the individual. The physiocrats pointed out that the main cause for all troubles and poverty in France was due to government interference. Therefore, they advocated minimum state interference. They thought that a state must provide universal education and it should also undertake public works.
Thus the functions of the physiocratic government were:
1. To preserve natural order.
2. To protect private property.
3. To spread education in natural order.
4. To undertake public works programme.
5. To eliminate international barriers.
In short, the physiocrats made the following contributions to economic theory:
a. They put economics on a scientific basis.
b. Their emphasis on the net product was notable.
c. Their analysis of capital pointed the true nature of that factor of production.
d. They made important contribution to the theory of taxation.
Thus the physiocrats by contributing many ideas occupied an important place in the history of economic thought. In-spite of their short period of life, their influence was more. Adam Smith got may ideas from the physiocrats.
The physiocrats must be given a high place among those who laid the foundation for the French Revolution. They were the pioneers in the field of distribution. Again, in the field of taxation, by suggesting a single tax on land they laid the principle of shifting and incidence of taxation.